Page 30 - 2021_03-Haematologica-web
P. 30
A.J. Ambinder and M. Levis
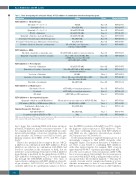
Table 1. Trials investigating the safety and efficacy of FLT3 inhibitors in combination with other therapeutic agents. Combination Setting
FLT3 Inhibitor + Chemotherapy:
Gilteritinib+7+3vs.7+3 NDAML
Phase
Phase III
Phase II Phase III Phase II Phase II Phase III Phase III Phase II
Phase III
Phase I/II
Phase I/II
Phase I/II
Phase I
Phase I/II
Phase I/II
Phase III Phase II Phase II
Phase I Phase I Phase I
Phase I Phase I/II
Clinical Trial Number
NCT02236013
NCT02283177 NCT02668653 NCT04209725 NCT03989713 NCT03250338 NCT03258931 NCT04047641
NCT02752035
NCT01892371
NCT03735875
NCT03661307
NCT03625505
NCT04140487
NCT03730012
NCT02997202 NCT02400255 NCT02927262
NCT03552029 NCT00819546 NCT03900949
NCT03904069 NCT02789254
Crenolanib + 7 + 3
Quizartinib + 7 + 3 vs. 7 + 3
CPX-351 + Quizartinib
Quizartinib + High dose Ara-C and Mitoxantrone Crenolanib + Chemotherapy vs. Chemotherapy alone Crenolanib + Chemotherapy vs. Midostaurin + Chemotherapy Cladribine, Idarubicin, Cytarabine, and Quizartinib
FLT3 Inhibitor + HMA:
Gilteritinib + Azacitidine vs. Azacitidine alone Quizartinib + Azacitidine or low-dose cytarabine
FLT3 Inhibitors + Novel Agents:
Venetoclax + Quizartinib
Quizartinib + Decitabine + Venetoclax
Venetoclax + Gilteritinib
Azacitidine + Venetoclax + Gilteritinib
Gilteritinib + Atezolizumab
FLT3 Inhibitors as Maintenance:
Gilteritinib vs. Placebo Crenolanib Gilteritinib
FLT3 Inhibitors + Investigational Agents:
Quizartinib + Milademetan (MDM2 inhibitor) FLT3 inhibitor (PKC412) + MTOR inhibitor (RAD001) Gemtuzumab + Midostaurin + 7 + 3
Immunotherapeutic Strategies:
FLT3 CAR-T AMG 553
Fc-optimized antibody (FLYSYN) to FLT3
ND mFLT3 AML
ND mFLT3-ITD AML
RR mFLT3-ITD AML
RR mFLT3-ITD AML
RR mFLT3 AML
ND mFLT3 AML
ND or RR AML, acute biphenotyic
leukemia or high risk MDS
ND mFLT3 AML, ineligible for intensive induction
Phase I, IIB cohorts: RR AML, MDS, or CMML Phase II cohort: ND or RR mFLT3 AML, MDS or CMML
RR mFLT3-ITD AML
ND or RR mFLT3 AML or MDS, ineligible
for intensive induction
RR AML
Phase I, IIB cohorts: RR mFLT3 AML or MDS,
Phase IIA cohort: ND AML RR mFLT3 AML
mFLT3 AML post-transplant maintenance mFLT3 AML post-transplant maintenance mFLT3 AML post-CR1 maintenance
ND and unfit for intensive induction or RR FLT3-ITD AML RR AML, MDS or CMML
ND mFLT3 AML
RR mFLT3 AML AML
HMA: hypomethylating agent; ITD: internal tandem duplications; AML: acute myeloid leukemia; MDS: myelodysplastic syndrome; CMML: chronic myelomonocytic leukemia; CR1: first com- plete remission; ND: newly diagnosed; RR: relapsed or refractory.
ing to hopes that combining HMA with newer and more potent FLT3 inhibitors may be even more effective.26,73 In two ongoing trials of quizartinib and gilteritinib in combi- nation with azacitidine or low-dose cytarabine (clinicaltri- als.gov identifiers: NCT01892371 and NCT02752035), pre- liminary analyses show ORR of 73% and 80%, respec- tively.74
There is also preclinical data to support the use of BCL- 2 inhibitors in combination with FLT3 inhibitors. BCL-2 inhibitors are effective in combination with HMA and low-dose cytarabine in the treatment of AML, but are ineffective as monotherapy. Resistance to BCL-2 inhibitor monotherapy is mediated by the upregulation of MCL-1. FLT3 inhibitors downregulate MCL-1 via reduced signal- ing through the RAS/MAPK pathway.75 Two trials of venetoclax in combination with FLT3 inhibitors (clinicaltri- als.gov identifiers: NCT03625505 and NCT03735875) are currently underway. In a preliminary analysis of the for-
mer, the ORR for patients with mFLT3 was 90%, despite the high rate of prior exposure to FLT3 inhibitors.76 Two other trials combining venetoclax with FLT3 inhibitors and HMA are also underway (clinicaltrials.gov identifier: NCT04140487 and NCT03661307).
As the armamentarium of targeted therapies grows, it is increasingly common to find mFLT3 alongside other druggable targets. The question that arises is whether or not there is any benefit to combining FLT3 inhibitors with other targeted agents. For example, FLT3 occurs in approximately 35-40% of patients presenting with APL.77 As is the case in almost every circumstance, mFLT3 APL has a worse prognosis. Interestingly, the worse prognosis associated with mFLT3 AML is mitigated when arsenic is incorporated into the treatment regimen.78,79 This may be a quirk of arsenic and its complex mechanism of action. Another circumstance is that of concomitant FLT3 and IDH mutations. Whether the addition of a FLT3 inhibitor
676
haematologica | 2021; 106(3)