Page 43 - 2020_11-Haematologica-web
P. 43
Pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia
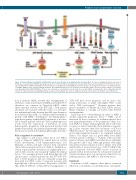
Figure 3. Kinase pathways deregulated in Philadelphia chromosome (Ph)-like acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). The diverse signaling alterations observed in Ph-like ALL are grouped into JAK-STAT activating lesions (most commonly CRLF2 rearrangement, but also JAK mutation and rearrangement, IL7R mutation, truncat- ing rearrangements of EPOR, and SH2B3 deletion/mutation), rearrangements involving ABL-class tyrosine kinases; rearrangements of genes encoding other kinas- es (FGFR1, NTRK3, FLT3), and Ras pathway mutations. Ras pathway mutations are not restricted to Ph-like ALL and are observed in other subtypes of leukemia (e.g., hyperdiploid ALL, PAX5 P80R ALL). They are also observed as co-mutations in a proportion of cases with CRLF2 rearrangements. These alterations typically activate the logical downstream signaling pathway, as well as other pathways that serve as additional avenues for therapeutic intervention (e.g., PI3K, BCL2).
tion of pediatric MPAL revealed that rearrangement of ZNF384 is common in B/myeloid MPAL and biallelic WT1 alterations are common in T/myeloid MPAL, which shares genomic features with ETP ALL.48 Such genetic alterations are consistent with the results of a retrospec- tive multinational study showing that ALL-type therapy is more effective than AML- or combined-type treatment in patients with MPAL.91 Furthermore, the immunopheno- typic heterogeneity within MPAL populations is not driv- en by distinct genomic subclones. Such a phenotypic fate results from the acquisition of mutations in early hematopoietic progenitors with preserved myeloid and lymphoid potentials, and individual phenotypic subpopu- lations can reconstitute the immunophenotypic diversity.48
TCF3-HLF have worse prognoses and are more com- monly adolescents or adults with higher WBC counts and/or CNS involvement.36,92 Hispanic patients have greater incidences of Ph-like ALL with CRLF2 fusions. Infant leukemia is strongly associated with KMT2A rearrangements.
Early response to chemotherapy in terms of MRD is another important prognostic factor.93,94 MRD can be measured by flow cytometry for leukemia-specific aber- rant immunophenotypes or by polymerase chain reac- tion (PCR) for unique immunoglobulin and T-cell recep- tor genes or fusion transcripts. Next-generation sequenc- ing is more sensitive than flow cytometry or PCR for MRD detection,95 but the superiority of this methodolo- gy for clinical application needs to be confirmed in larger studies. The relapse risk at a given MRD level differs between genetic subtypes.93,94 Patients with favorable genetic subtypes clear MRD faster than those with high- risk genetics and T-ALL. Although patients with high- risk genetic features remain at risk for relapse even with undetectable or very low level (e.g., <0.01%) MRD at the end of induction, low-level MRD can be overcome in patients with low-risk features by subsequent treatment. Current treatment protocols incorporate clinical factors, leukemia genetics, and MRD for risk-stratification.
Treatment
Treatment of ALL comprises three phases: remission induction, consolidation (or intensification), and mainte-
Risk assignment for treatment
Age (infant or ≥10 years), white blood cell (WBC) count at diagnosis (≥50x109/L), central nervous system (CNS) involvement, T-cell immunophenotype, race (Hispanic or black), and male sex have been considered clinical adverse prognostic factors (Table 3). Furthermore, certain somatic genetic alterations are significantly asso- ciated with outcome and can partly explain the clinical factors.15 For example, patients with hyperdiploidy (>50 chromosomes or DNA index≥1.16) and ETV6-RUNX1 have a better prognosis and are commonly young chil- dren with low WBC counts. Conversely, patients with hypodiploidy (<44 chromosomes), Ph-positive or Ph-like ALL, KMT2A, MEF2D, or BCL2/MYC rearrangements, or
haematologica | 2020; 105(11)
2531