Page 17 - 2020_11-Haematologica-web
P. 17
Editorials
AB
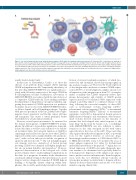
Figure 1. On- and off-target toxicities from antibody-drug conjugates (ADC) within the lymphoma microenvironment. (A) Schematic ADC, consisting of an antibody, a linker and the cytotoxic payload. Endocytosis of the ADC and linker cleavage will release the payload, resulting in cytotoxic effects. (B) On- and off-target cytotoxic effects from payload release with or without ADC internalization in a tumor microenvironment with abundant but heterogeneous expression of the target antigen. Payloads might be cleaved without endocytosis and/or permeate cell membranes to be taken up by bystander cells, thus facilitating drug efficacy even in tumor cells without adequate antigen expression. Toxic effects from microtubule-targeted compounds like maytansine on non-proliferating cells are typically reduced as compared to highly prolifer- ating malignant cells (blue) with activated cell cycle checkpoints.
usually tried in basket trials).2
In this issue of Haematologica, Gaudio et al. show the
efficacy of an antibody drug conjugate (ADC) targeting CD205 in lymphoma models.6 Importantly, the efficacy of this new drug, MEN1309/OBT076, was significantly asso- ciated with cell surface expression of the target CD205 in B-cell lymphoma cell lines. Furthermore, cytotoxicity of MEN1309/OBT076 was reduced with the introduction of a competitive CD205 antibody. These findings underline the dependence of drug efficacy on target availability, sug- gesting the potential of CD205 expression as a predictive biomarker. In an in vitro screen, MEN1309/OBT076 effica- cy did not depend on B-cell lymphoma subtype. Together with previous preclinical results in CD205-positive triple- negative breast, pancreatic and bladder cancer cell lines and xenografts,7 this creates a virtual preclinical basket trial which now awaits clinical validation.
However, several questions remain to be answered for the clinical development of MEN1309/OBT076 in lym- phoma. In addition to its predictive significance in preclin- ical models (that, as we have said, still needs to be validat- ed in clinical trials), the biological function of CD205 is surprisingly unclear. Previous reports show that CD205 is expressed on leukocytes, mainly dendritic cells and mono- cytes8,9 with a role in endocytosis and the recognition of apoptotic and necrotic cells.10,11 The role in lymphomagen- esis remains even less understood. A fusion protein involving CD205 was identified in Hodgkin lymphoma12 but also in normal dendritic cell maturation.10 However, improved characterization of the biological role of this protein remains vital to understanding its implications in the clinic (as a prognostic biomarker in the identification of adequate clinical settings for the introduction of a novel drug) as well as a diagnostic biomarker. If CD205 helps in defining a biologically distinct subgroup within lym- phomas, this would be particularly relevant for the identi-
fication of rational combination partners, of which two, venetoclax and rituximab, showed promising signals in the study by Gaudio et al.6 However, the broad expression of the antigen with a moderate to intense CD205 expres- sion in 20-50% of tested lymphoma samples, and an over- all expression of the antigen in more than 70% of samples, makes it unlikely that CD205 adequately reflects lym- phoma heterogeneity, and stability of CD205 protein expression needs to be validated. Stable expression of the antigen is probably linked to continued efficacy of the drug, following the successful examples of other ADC such as brentuximab vedotin (targeting CD30),13 polatuzumab vedotin (targeting CD79b),14 or trastuzumab emtansine (targeting HER2).15 Efficacy of trastuzumab emtansine could still be demonstrated despite previous HER2-directed therapies and retreatment with brentux- imab vedotin showed responses in the majority of patients that had relapsed after initial response to the same drug.16 In the work by Gaudio et al.,6 a rechallenge with MEN1309/OBT076 was also sufficient to induce remission in the only xenograft model with tumor regrowth after a first dose of the ADC. These and other data support the further development of ADC as powerful tools for the targeted delivery of cytotoxic drugs. Interestingly, neither resistance to CD30-directed ADC or to HER2-directed ADC seems to be mediated by a loss of target antigen expression but rather by dysfunctional intracellular metabolism of the payload.17,18 Again, the con- tinued expression of CD205 even under therapeutic pres- sure remains to be determined and is probably linked to its biological role. Expression of the antigen is also impor- tant to predict toxicities in human trials. Even though pre- vious work has not identified relevant toxicities in cynomolgus monkeys,7 potential risks to humans will also depend on disease characteristics and are still to be deter- mined in ongoing clinical trials.
haematologica | 2020; 105(11)
2505