Page 164 - 2020_09-Haematologica-web
P. 164
T. Abache et al.
AB
CDE
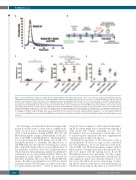
Figure 7. In vivo evaluation of actiten in a rabbit model of antibody-induced hemophilia A. (A) In vitro control of the efficiency of anti-factor VIII (FVIII) antibodies. Thrombin generation was induced by tissue factor/phospholipids in rabbit normal plasma (NP) in the presence or absence of anti-FVIII inhibitors (3 μg/mL each). (B) Schematic representation of the in vivo protocol. The rabbit’s paw is placed in phosphate-buffered saline at 37°C to measure time to clot and to collect blood loss. (C) Evaluation of rabbit bleeding following infusion of anti-FVIII antibodies. Bleeding times were recorded in rabbits infused with NaCl (n=8) or anti-FVIII antibodies (99 μg/kg each; n=4) following a nail cuticle cut. Data are presented as the means ± standard error of mean (SEM) and are representative of at least two separate experiments. (D) Evaluation of actiten potency in rabbits infused with anti-FVIII inhibitors. Bleeding times were recorded from rabbit controls (n=4), rabbits infused with anti-FVIII inhibitors and NaCl (n=7) or actiten (1.7 mg/kg, n=3) or recombinant wildtype factor X (recFX-WT) (1.7 mg/kg, n=4) or recombinant activated factor VII (recFVIIa) (500 μg/kg, n=6) following a nail cuticle cut. (E) Hemoglobin loss from rabbits infused with anti-FVIII inhibitors and NaCl (n=7) or actiten (1.7 mg/kg, n=3) or recFX-WT (1.7 mg/kg, n=4) or recFVIIa (500 μg/kg, n=4). Data are presented as the means ± SEM (statistical significance: ns: not significant; *P<0.05, **P<0.01). (D, E) Experiments were performed in two distinct rounds that are identified by the marker color. NP: normal plasma; MoAb: monoclonal antibodies; ND, not done.
The advantages of actiten include the interesting possibil- ity that it could be used to correct various coagulation dis- orders. At a dose close to the physiological concentrations of FX, actiten normalizes clotting in FVIII-, FIX-, FX- and FXI-deficient plasma samples, independently of the pres- ence of anti-FVIII or anti-FIX inhibitors. Thrombin genera- tion assays performed in rabbit plasma were found to be remarkably predictive to determine the efficient dose of anti-FVIII antibodies, the effective concentrations of actiten and to help in the design of the in vivo assay. On the basis of this experience, corrections of the other coagulation defects observed in factor-deficient plasma samples would likely be confirmed in vivo in other preclinical models. Whereas the hemophilia A and B markets stimulate the research for innovative treatments, this is not true for FX and FXI defi- ciencies. Recently, a recombinant version of FX was offered to patients whereas FXI deficiency can only be treated by a few plasma-derived products.28,29 Given its limited activa-
tion by the tenase complex, it could be expected that replac- ing FX by actiten might be less efficient than replacing it with natural FX, despite promising in vitro data. Nevertheless, if the in vivo potential of actiten turns out to be satisfactory, the compound could offer a supplementary treatment option for these rare diseases.
Modifying the specificity of FX could induce a risk of thrombogenicity. However, no sign of such a drawback has been identified so far. In vitro incubation of the mole- cule in FVIII- and FX-deficient plasma samples without induction led to clotting at later times than when the sam- ples were spiked with the missing factors. In all the thrombin generation assays performed, once the coagula- tion was initiated it was systematically controlled by the anticoagulation system since all peaks returned to base- line. In vivo, the rabbits showed no clinical signs of suffer- ing and the markers of thrombosis measured remained at baseline levels. In addition, the infusion of actiten (at 0.33
2342
haematologica | 2020; 105(9)