Page 108 - Haematologica May 2020
P. 108
M.N. Peiris et al.
the Hsp90 chaperone system to avoid ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation.28 Here, we aim to uncover if BCR-FGFR1 is a client of Hsp90 and possibly relies on the Hsp90 complex for stability and cellular survival.
HEK293T cell lysate expressing either FGFR1 or BCR- FGFR1 derivatives were immunoprecipitated with FGFR1 antisera and immunoblotted for Hsp90. An interaction was observed between Hsp90 and BCR-FGFR1 deriva- tives (Figure 6A). To further analyze if BCR-FGFR1 is dependent on Hsp90 for cellular stability and activity, assays with potent Hsp90 inhibitor, Ganetespib, were performed. HEK293T cells expressing either FGFR1 or BCR-FGFR1 derivatives were treated with 200 nM Ganetespib for 4 h, then analyzed for overall FGFR1 expression and activation of downstream cell signaling pathways (Figure 6B). A significant reduction in BCR- FGFR1 expression is observed following Ganetespib
Table 1. Biological activity of mutations in phosphoacceptor sites. Construct Foci relative to SEM (%)
BCR-FGFR1 (%)
Mock 00
BCR-FGFR1 100 11
BCR(Y177F)-FGFR1 55 16
BCR(Y436F)-FGFR1 120 2
BCR(Y455F)-FGFR1 108 9
BCR(S122A)-FGFR1 97 1
BCR(Y246F)-FGFR1 105 7
BCR(S459A)-FGFR1 129 1
BCR(Y554F)-FGFR1 126 11
BCR(T359A/S367A/S369A/S377A)-FGFR1 129 3
BCR: breakpoint cluster region; FGFR1: fibroblast growth factor receptor 1; SEM: stan- dard error of the mean.
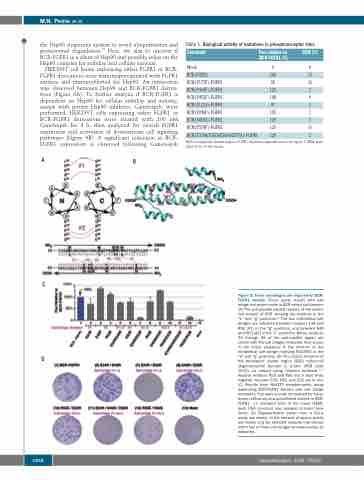
A
B
C
D
Figure 5. Three salt bridges are required for BCR- FGFR1 activity. Focus assay results with salt bridge mutations made in BCR coiled-coil domain. (A) The anti-parallel heptad repeats of the coiled- coil domain of BCR showing the residues in the “e” and “g” positions.23 The two interhelical salt bridges are indicated between residues E34 and R55 (#1) in the “g” positions, and between E46 and R53 (#2) in the “e” positions. Below, residues 30 through 65 of the anti-parallel region are shown with the salt bridges indicated. Also shown in the linear sequence is the location of the intrahelical salt bridge involving E52-R55 in the “d” and “g” positions. (B) The crystal structure of the breakpoint cluster region (BCR) coiled-coil oligomerization domain is shown (PDB code 1K1F), as viewed using Chimera software.24,25 Positive residues R53 and R55 are in blue while negative residues E34, E46, and E52 are in red. (C) Results from NIH3T3 transformation assay expressing BCR-FGFR1 fusions with salt bridge mutations. Foci were scored, normalized for trans- fection efficiency and quantitated relative to BCR- FGFR1 –/+ standard error of the mean (SEM). Each DNA construct was assayed at least three times. (D) Representative plates from a focus assay are shown. In the interest of space, plates are shown only for selected mutants that disrupt either two or three salt bridges simultaneously, as indicated.
1268
haematologica | 2020; 105(5)