Page 34 - Haematologica Atlas of Hematologic Cytology
P. 34
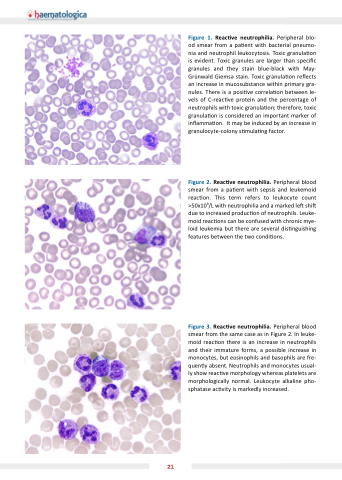
Figure 1 Reac ve neutrophilia Peripheral blo- od smear from a a a a a pa ent with bacterial pneumo- nia and neutrophil leukocytosis Toxic granula on is evident Toxic granules are larger than speci c c c granules and they stain blue-black with May- Gr nwald Giemsa stain Toxic granula on re ects an an increase in in in mucosubstance within primary gra- nules There is a a posi ve correla on between le- vels of of C-reac ve ve protein and the percentage of of neutrophils with toxic toxic granula on therefore toxic toxic granula on on is considered an an an important marker of in in in in amma on It may be induced by an increase in in in in granulocyte-colony s
mula ng factor Figure 2 Reac ve neutrophilia Peripheral blood smear from a a a a pa ent with sepsis and leukemoid reac on This term refers to leukocyte count >50x109/L with neutrophilia and a a a a marked le shi due to increased produc on of neutrophils Leuke- moid reac ons
can be confused with chronic mye- loid leukemia but there are several dis nguishing features between the two condi ons
Figure 3 Reac ve neutrophilia Peripheral blood smear from the same case as as in Figure 2 In leuke- moid reac on there is an increase in in neutrophils and their immature forms a a a a possible increase in in monocytes but eosinophils and basophils are fre- quently absent Neutrophils and monocytes usual- ly show reac ve morphology whereas platelets are morphologically normal Leukocyte alkaline pho- sphatase ac vity is markedly increased 21