Page 20 - Haematologica Atlas of Hematologic Cytology
P. 20
ABAB
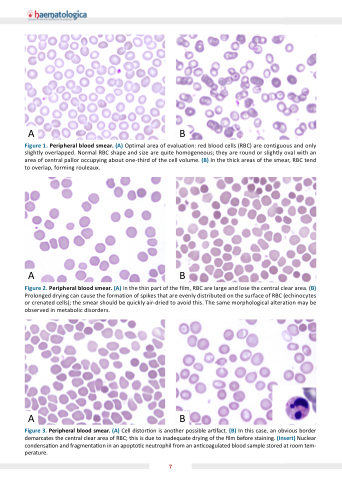
Figure 1 Peripheral blood
blood
smear (A) Optimal area of evaluation: red blood
blood
cells (RBC) are are are are contiguous and and only slightly slightly overlapped Normal RBC RBC RBC shape and and size are are are are are are quite homogeneous they are are are are are are round or or or slightly slightly oval with an an an area area of of of central pallor occupying about one-third of of of the the the the cell volume (B) In the the the the thick areas of of of the the the the smear RBC RBC tend to overlap forming rouleaux ABAB
Figure 2 Peripheral blood
smear (A) In the the the the the thin part of of of the the the the the film RBC RBC are are are large and lose the the the the the central clear area (B) Figure Peripheral blood
smear (A) A and an an (B) and a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a Prolonged drying can cause the the the the the the formation of of of spikes that are are are evenly distributed on on on on the the the the the the surface of of of RBC RBC (echinocytes and or or or or crenated cells) the the the smear should be be quickly air-dried to avoid this The same morphological alteration may be be observed in metabolic disorders ABAB
Figure 3 Peripheral blood
smear (A) Cell distor on is is is is is another possible ar ar ar ar ar ar fact (B) In In this this case an an obvious border demarcates the the the central clear clear area of of RBC this this is is is is is due to to to to inadequate drying of of the the the lm before staining (Insert) Nuclear condensa on on on and fragmenta on on on in in in in in an an an an apopto c c c c c c c neutrophil from an an an an an an an an coagulated blood
sample stored at at at at at room tem- perature 7