Page 81 - 2019_03-Haematologica-web
P. 81
NRF2 and Ara-C resistance in MDS
MDS patients with higher and lower NRF2 levels (Online Supplementary Table S2).
Pharmacological modulations of NRF2 regulate chemotherapeutic efficacy of Ara-C in MDS cells
The effect of NRF2 on Ara-C resistance was first evalu- ated in primary MDS cells. After 72 h exposure to increas- ing doses of Ara-C, proliferation of primary MDS cells with 2 mM NRF2 inhibitor Luteolin was significantly reduced compared to vehicle control-treated MDS cells (# 1 MDS-EB-2 IC50: 5.7 mM vs. 4.8 mM, P=0.04; # 2 MDS- EB-2 IC50: 3.2 mM vs. 1.9 mM, P=0.006; # 3 MDS-EB-2 IC50: 7.5 mM vs. 6.9 mM; P=0.03) (Figure 2A).
To further identify the function of NRF2 in MDS, we examined the pharmacological effects of NRF2 inhibitor and activator in MDS-patient-derived SKM-1 and murine MDS model cells MLLPTD/WT/RUNX1-S291fs cells.20 The highest dose of Ara-C resulted in approximately 90% inhibition of SKM-1 at 72 h (IC50, 1.72 mM) and MLLPTD/WT/RUNX1-S291fs cells at 48 h (IC50, 0.17 mM) (Online Supplementary Figure S2A and B). In agreement with previous reports on human lung carcinoma and col-
orectal cancer cell lines,21,22 we found that the NRF2 inhibitor Luteolin (3, 4, 5, 7-tetrahydroxy flavone) sup- pressed the protein expression of NRF2 in SKM-1 (Figure 2B). Sulforaphane (SFN) has been shown to be a potent NRF2 activator.23 SFN treatments in SKM-1 cells increased the protein expression of NRF2 (Figure 2C). NRF2 mRNA levels in MDS cells treated with the NRF2 inhibitor or ago- nist were measured. There was little change at mRNA levels, but obvious changes of NRF2 were seen at protein levels (Online Supplementary Figure S2C-F). Lower doses of Luteolin treatment had little effect on cell proliferation (Online Supplementary Figure S3A), but significantly enhanced the cytotoxicity of Ara-C (0-4 mM) to SKM-1. The IC50 values of Ara-C in SKM-1 cells were 1.41 mM and 0.93 mM with 5 mM and 10 mM Luteolin treatment, respectively (P<0.001) (Figure 2D). Similar results were also found in MLLPTD/WT/RUNX1-S291fs cells (Online Supplementary Figure S3B-D). The IC50 was reduced from 0.17 mM to 0.11 mM by 1 mM Luteolin in MLLPTD/WT/RUNX1-S291fs (P=0.007) (Online Supplementary Figure S3D). 1mM SFN treatments had little effect on the proliferation of SKM-1 cells (Online Supplementary Figure
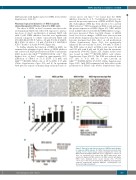
A
BC
D
Figure 1. Expression and clinical outcomes of NRF2 in myelodysplas- tic syndrome (MDS) patients. (A) NRF2 immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining of bone marrow biopsy samples (magnification ×400). (B) MDS patients had higher NRF2 IHC scores compared to controls. (C) Gene set enrichment plot showed that NRF2 target genes were enriched in higher-risk MDS patients. (D) MDS patients with higher NRF2 levels displayed worse overall survival (OS). *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P≤0.001. Int: intermediate; MDS-SLD: myelodysplastic syndrome single-lineage dysplasia; MDS-RS: myelodysplastic syn- drome with ring sinderoblasts.
haematologica | 2019; 104(3)
487