Page 183 - 2019_03-Haematologica-web
P. 183
Effect of VWF mutations on mRNA splicing
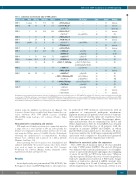
Table 1. Laboratory and molecular data of VWD patients
Patients code
UMP01
UMP02
UMP03
UMP04 UMP05 UMP06
UMP07
UMP08
UMP09‡ UMP10 UMP11
UMP12
UMP13
VWD VWF:Ag
3 carrier 70
1H 36
1 26
1 50
1 27
2A/2M 12
1 37
1 42.4
1 51 3 carrier 46.4
1 31
3 3.7
2A 117
VWF:RCo FVIII:C NT change
70.5 111 c.1533+1G>A
AA change Exon
Intron Domain
13 intronic
49 101
21.2 64.8
52 47 32 72 4 24
28 60
c.3379+1G>A *
c.-2627C>T *
c.5664+2T>C *
c.7220T>C *
c.7081+6G>T c.7730-56C>T c.4120C>T * c.7730-4C>G * c.8254-5T>G
- -
25 intronic
- -
- -
- upstream 33 intronic - C2
41 intronic 45 intronic
- -
p.Leu2407Pro 42
- -
- -
p.Arg1374Cys 28 A1
- -
45 intronic 51 intronic - D1
- A1-A3 - D3
- -
41.7 73.4 c.546G>A† c.4866C>T†
p.Ser182 6
p.Asp1622 28 49.8 71 c.3291C>T p.Cys1097 25
- D1 - D3
45 24
5
6.5
105 c.1109G>A
57 c.3223-7_3236dup
6.7 c.449T>C† c.7082-2A>G†
90 c.3426T>C§ c.3485_3486delinsTG§
c.8318G>C†
4,5 c.6699_6702dup† c.7437G>A†
5 c.546G>A§ c.7082-2A>G§ c.8155+3G>C†
p.Cys370Tyr 9 p.Pro1079_Tyr1080ins 25
LeuGlnValAspProGluPro
- D1 41 intronic - D3
- D3
- CK
- D4
- C3
- D1 41 intronic 50 intronic
p.Leu150Pro 5
- -
UMP14 1
UMP15|| 3
6 6
2 <1
p.Cys1142 26 p.Pro1162Leu 26 p.Cys2773Ser 52
p.Cys2235ArgfsTer8 38
p.Ser2479 43 p.Ser182 6 - - - -
All mutations were identified in heterozygous state.In bold,mutations selected to study their effect on VWF mRNA.The subtype 1H (historical) refers to patients previously diag- nosed as type 1VWD that,at the time of enrollment at the PCM-EVW-ES project,show a slight decrease or even a normalVWF plasma levels.AA:amino acid;NT:nucleotide;VWD: von Willebrand disease. *The allelic phase (cis/trans) of mutations could not be determined since no informative relatives are available. †Mutations in trans. ‡Patient with an addi- tional mutation in the F8 gene. §Mutations in cis. ||Patient previously studied at mRNA level by Corrales et al.7
purified using the MiniElute Gel Extraction kit (Qiagen). The sequences obtained were assembled and aligned against the con- sensus wild-type (WT) VWF mRNA sequence (GenBank NM_000552) using SeqScape v2.7 software (Thermo Fisher Scientific).
Next-generation sequencing and analysis
PCR amplicons obtained per patient were equimolarly mixed in a single tube in a total amount of 250 ng. Subsequently, the libraries were fragmented and the adapter and barcodes were lig- ated using the NGSgo protocol (GenDX, Utrecht, Netherlands) following the manufacturer’s recommendations. Resulting libraries were combined and sequenced on a MiSeq platform (Illumina, San Diego, CA).
After sequencing, barcoded sequences were demultiplexed and analyzed individually. The paired sequence files (fastq format) were used as input for analysis with the CLC Genomic Workbench v.11 software (Qiagen, Aarhus, Denmark) (Online Supplementary Methods and Figure S1-S2).
Results
An in-depth study was performed in PCM-EVW-ES,3 the Portuguese cohort,4 and HUVH patients to select previous-
ly undescribed VWF mutations and mutations with an unknown or controversial pathogenic mechanism. Eighteen mutations (15 patients) were selected: 8 intronic (4 in canonical, GT and AG, splice site sequences), 5 syn- onymous, 2 missense, and 3 delins. The patients’ pheno- typic and molecular data are summarized in Table 1 and Online Supplementary Table S2. Total mRNA was obtained from platelets and leukocytes of all patients, with the exception of patients UMP08 and UMP14, in whom platelet RNA isolation failed due to blood lysis. All muta- tions were analyzed by both Sanger sequencing and NGS, and results were compared to the predictions generated by in silico analysis (Online Supplementary Table S3).
Mutations in canonical splice site sequences
The c.1533+1G>A mutation (intron 13) was identified in a type 3 VWD carrier (UMP01). The exon 11-15 region was analyzed with a specific primer pair to avoid amplifi- cation of a prevalent alternative-splicing product (skipping of exons 14 and 15) in VWF from leukocytes.7 Whereas only the expected PCR product was observed in platelets, leukocyte amplification resulted in 4 PCR bands. Sanger analysis of leukocytes showed 2 mRNA aberrant tran- scripts: 1) lacking exon 13; and 2) lacking exon 13 and 14 (Online Supplementary Figure S3). By means of NGS, it was
haematologica | 2019; 104(3)
589