Page 172 - 2019_03-Haematologica-web
P. 172
N. Giménez et al.
erythrin (Becton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) (Online Supplementary Methods).
Statistical analysis
A Fisher test or non-parametric tests were used to correlate clinical and biological variables according to the presence of mutations in the RAS-BRAF-MAPK-ERK pathway. Time to first treatment (TTFT) was calculated from the date of sampling to the first treatment or last follow-up. Overall survival was calcu- lated from the date of sampling to the date of death or last fol- low-up. All the analyses were conducted using SPSS 20 (www.ibm.com) software and are detailed in the Online Supplementary Methods. For primary cell cultures data are pre- sented as the mean ± standard error of the mean. Comparisons between groups were evaluated with a Wilcoxon paired test using GraphPad Prism 4.0 software. Results were considered sta- tistically significant when the P-value was ≤0.05.
Results
Clinical and biological impact of mutations in the RAS- BRAF-MAPK-ERK pathway
Four hundred fifty-two patients (276 males/176 females) with CLL were analyzed for the clinical and bio- logical impact of mutations in genes of the RAS-BRAF- MAPK-ERK pathway (see Online Supplementary Table S1 for the main characteristics of the series).
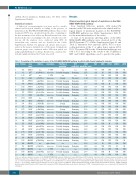
A total of 31 mutations affecting genes of the RAS- BRAF-MAPK-ERK pathway were observed in 30 of the 452 CLL patients (7%) (Online Supplementary Figure S1 and Table 1). Mutations were missense (25/31; 81%) or non- coding mutations at the 3’ or splice donor regions (6/31; 19%). The mean VAF for the 31 individual mutations was 0.36 ± 0.13. According to the results of the PolyPhen-2, SIFT and CADD algorithms used to predict the patho-
Table 1. Description of the mutations in genes of the RAS-BRAF-MAPK-ERK pathway in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Case Patient Gene HGVS.p Annotation PolyPhen-2 SIFT CADD VAF IGHV TP53 BIRC3 ATM
1
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9* 10 11 12 13 9* 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29
30
3' UTR
missense 3' UTR missense missense missense missense missense missense missense 3' UTR missense missense missense missense missense missense missense missense missense missense missense missense missense missense missense splice donor missense 3' UTR
442 MAPK1 n.a. 3' UTR
name
723 KITLG 33 KIT 1078 KIT
predictiona
n.a.
Probably damaging n.a.
predictionb
n.a.
Damaging n.a.
phred-like scorec
4.25 0.39
22.70 0.24
5.91 0.55
10.21 0.50
32.00 0.58
33.00 0.54
28.20 0.17
28.20 0.50
31.00 0.15
28.10 0.42
1.21 0.31
29.90 0.18
23.50 0.42
25.30 0.30
23.10 0.22
34.00 0.15
24.50 0.20
27.50 0.54
24.30 0.38
29.70 0.49
19.38 0.48
28.80 0.25
32.00 0.33
34.00 0.46
29.10 0.19
32.00 0.29
23.30 0.39
24.70 0.26
11.64 0.43
27.00 0.33
12.71 0.43
n.a.
p.Val833Leu n.a.
UM UM MM
850 SOS2 p.Pro7Ser
Benign Tolerated
M UM UM UM M UM M UM
UM M UM UM UM UM UM UM UM UM UM UM UM UM UM UM UM UM UM UM UM UM UM UM UM UM UM UM UM M UM UM UM UM UM UM UM UM UM UM UM UM
M UM UM UM M UM
UM M UM UM
UM UM
UM UM
UM UM
UM UM
UM UM
UM UM
UM UM
UM UM
UM UM
UM UM
UM UM
UM UM
UM UM
UM UM
UM UM
UM UM
UM UM
UM UM
UM UM
UM UM
UM UM
UM UM
UM UM
UM UM
UM M
UM UM
M M
UM UM
UM UM
UM UM
191 PTPN11 677 PTPN11 1192 PTPN11 1226 PTPN11 155 PTPN11 15 GNB1
p.Ala72Val p.Glu76Lys p.Asp61Val p.Asp61Val p.Ser502Pro p.Ile80Thr n.a. p.Gly12Val
Probably damaging Probably damaging Probably damaging Probably damaging Possibily damaging Probably damaging n.a.
Probably damaging
Benign
Possibily damaging
Benign
Probably damaging
Possibily damaging
Probably damaging
Possibily damaging
Probably damaging
Probably damaging
Probably damaging
Probably damaging
Possibily damaging
Probably damaging
Probably damaging
n.a.
Probably damaging
n.a.
Probably damaging
n.a.
Damaging Damaging Damaging Damaging Damaging Damaging n.a. Damaging Damaging Damaging Damaging Damaging Damaging Damaging Damaging Damaging Damaging Damaging Damaging Damaging Damaging Damaging n.a. Damaging n.a. Damaging n.a.
1564 GNB1
398 KRAS
598 KRAS p.Gln61His 155 KRAS p.Gly12Asp
1371 NRAS p.Gln61Arg
27 BRAF 100 BRAF 134 BRAF 148 BRAF 279 BRAF 721 BRAF 824 BRAF 1079 BRAF 1431 BRAF
44 MAP2K1 1365 MAP2K1 884 MAP2K2 761 MAP2K2 1477 MAP2K2 1568 MAP2K2
p.Glu501Lys
p.Lys601Glu
p.Gly469Ala
p.Lys601Asn
p.Asp594Gly
p.Asn581Ser
p.Leu597Gln
p.Val600Glu
p.Gly534Arg
p.Phe53Cys
p.Gly128Asp
n.a.
p.Gln60Pro
n.a.
p.Tyr134Cys missense
*CLL case with two mutations in genes of the RAS-BRAF-MAPK-ERK pathway; aAdzhubei I, Jordan DM, Sunyaev SR. Predicting functional effect of human missense mutations using PolyPhen-2. Curr Protoc Hum Genet. 2013; Chapter 7: Unit 7.20. bNg PC, Henikoff S. SIFT: Predicting amino acid changes that affect protein function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003 Jul 1;31(13):3812-4. cKircher M, Witten DM, Jain P, O'Roak BJ, Cooper GM, Shendure J. A general framework for estimating the relative pathogenicity of human genetic variants. Nat Genet. 2014;46(3):310-5. HGVS.p: Human Genome Variation Society protein sequence; PolyPhen-2: Polymorphism Phenotyping v2; SIFT: Sorting Intolerant From Tolerant; CADD: Combined Annotation-Dependent Depletion; VAF: variant allele frequency; IGVH: immunoglobulin variant heavy chain genes; 3’UTR: 3’ untranslated region; n.a. not applicable; M: mutated, UM: unmutated.
578
haematologica | 2019; 104(3)