Page 185 - 2020_08-Haematologica-web
P. 185
Apoptosis induced by selective BH3-mimetics
but low levels of BCL-2 and MCL-1, which may explain why BCL-XL was the preferred binding partner. Treatment with A1331852 displaced both BAX, BAK and BIM from BCL-XL. Knockdown experiments indicated that although BIM was displaced, it did not contribute to A1331852-induced apoptosis, whereas both BAX and
BAK were involved. Taken together, these experiments indicate that the marked sensitivity of RCK8 and SUDHL8 cells reflected the high levels of BAX and BAK bound by BCL-XL and that the displacement of these pro- teins by A1331852 was sufficient to induce apoptosis. Another study has shown a requirement for BH3-only
ABC
DEF
GHI
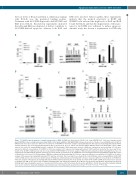
Figure 7. S63845 induced apoptosis is mainly independent of BAK. (A) BAK was deleted from U2946 cells using CRISPR/Cas9. Cells were transduced with pLentiCRISPRv2 either carrying non-human target (NHT) control guide (g)RNA or BAK gRNA (BAK) followed by selection of stable clones with BAK deletion. NHT or BAK-deleted clones were exposed to different concentrations of S63845 for 4 h before analysis of phosphatidylserine (PS) exposure by staining with annexin V-FITC and flow cytometry. The mean and standard deviation (SD) are shown (n=3). (B. C) To achieve efficient knockdown, BAX was silenced in U2946 NHT control or BAK- deleted cells (clone 12) using siRNA#1 and #3 combined. (B) Knockdown of BAX and genetic deletion of BAK was confirmed by western blotting. (C) Cells were exposed to different concentrations of S63845 for 4 h before analysis of PS exposure by staining with annexin V-FITC and flow cytometry. The mean and SD are shown (n=4). (D) NHT or BAK-deleted cells were treated with 100 nM S63845 for 4 h before analysis of BAX activation using intracellular staining with an active con- formation-specific BAX antibody and flow cytometry. The mean and SD are shown (n=3). (E, F) BIM was silenced using short-interfering (si)RNA in U2946 NHT control or BAK-deleted cells (clone 12). (E) Knockdown of BIM was confirmed by Western blotting. (F) Cells were exposed to different concentrations of S63845 for 4 h before analysis of PS exposure by staining with annexin V-FITC and flow cytometry. The mean and SD are shown (n=4). (G, H) NOXA was silenced using siRNA in U2946 NHT control or BAK-deleted cells (clone 12). (G) Knockdown of NOXA was confirmed by western blotting. (H) Cells were exposed to different concentrations of S63845 for 4 h before analysis of PS exposure by staining with annexin V-FITC and flow cytometry. The mean and SD are shown (n=4). (I) NHT or BAK-deleted clones were exposed to S63845 (100 nM) for 4 h before lysis in CHAPS-containing buffer and immunoprecipitation (IP) of MCL-1. The interaction with NOXA is demonstrated by western blotting. Input lanes showing the presence of overall protein in the lysate, and IP lanes show the interaction with MCL-1. Protein G beads without primary antibody were used to control for unspecific binding. A representative blot of two independent experiments is shown. *P<0.05;**P<0.01; ***P<0.001.
haematologica | 2020; 105(8)
2161