Page 150 - 2020_08-Haematologica-web
P. 150
Y. Saito et al.
A
BCD
E
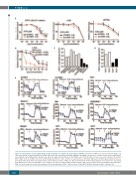
Figure 5. L-asparaginase (L-asp) inhibits EVI1-mediated activation of oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS). (A) Survival of MF9 acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells after brief exposure to glycolysis inhibitors (STF31 and 2-DG) and a glutaminolysis inhibitor (BPTES). Evi1/MF9 cells were more sensitive to glycolysis and glutaminol- ysis inhibitors than wild-type (WT) leukemia cells. (B) L-asp suppressed proliferation of Evi1/MF9 cells. (C) EVI1high AML cell lines were more sensitive to L-asp than EVI1low AML cell lines. (D) AML cells from two EVI1+ AML patients were more sensitive to L-asp than those from EVI1- AML patients. (E) Energy metabolism was ana- lyzed by the XFp extracellular flux analyzer after L-asp treatment (1 U/mL) of AML cells. Basal and maximum OCR in mitochondria were much lower in L-asp-treated Evi1/MF9 than in L-asp-treated WT/MF9 cells. L-asp does not suppress mitochondrial oxidation in EVI1low AML cell lines (THP1, Kasumi-1 and NB4) and primary EVI1– AML cells. L-asp suppressed basal and maximum OCR in mitochondria of EVI1high AML cell lines (UCSD/ANL1, MOLM1) and primary EVI1+ leukemia cells.
2126
haematologica | 2020; 105(8)