Page 231 - 2020_07-Haematologica-web
P. 231
Bleeding disorders in heavy menstrual bleeding
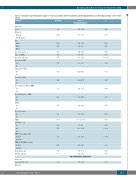
Table 3. Univariate and multivariate analyses of the association between baseline patient characteristics and bleeding disorder in the entire cohort.
Parameter
Intercept
Age, y Ethnicity
Hispanic
Non-Hispanic
Race
White Black Other
Age at menarche, y Time to HMB, y Age at first bleed, y Refractory HMB
Yes
No
Surgical bleeding
Yes
No
Dental bleeding
Yes
No
Presentation to ED for HMB
Yes
No
Hospitalization for HMB
No
Yes pRBC Yes No
Need for IV iron
Yes
OR for BD
0·98 1.95
1·74 1·38
1.02 0·84 0·74
1·72
4·57
5·42
0·50
2.03
0·55
1·39
95% CI UNIVARIATE ANALYSIS
0.84, 1.14 1.03, 3.70
0.45, 6.65 0.32, 5.90
0.84, 1.25 0.65, 1.09 0.66, 0.84
0.90, 3.30
1.28, 16.31
1.02, 28.78
0.26, 0.97
0.93, 4.42
0.24, 1.24
0.76, 2.54
1.0001, 1.002
0.70, 4.7 1.91, 10.64
1.61, 6.42
1.16, 4.29
0.97, 1.01
0.97, 1.02
MULTIVARIATE ANALYSIS
0.73, 0.96
P
0.802 0.038
0.416 0.665
0.789
0.199 <0.0001
0.099
0.019
0.047
0.042
0.072
0.151
0.275
0.036
0.217 0.0006
0.0007
0.015
0.752 0.980
0.011
No
PBAC 1·001 ISTH BAT score
≥3 ≥4 ≤2
FMH of bleeding or BD Positive
Negative
FMH of GYN/OB bleeding Positive
Negative
Hemoglobin, g/L Ferritin, pmol/L
Intercept
Age at first bleed, y Ethnicity
1·83 4·51
3.09
2·23
0.99 1.00
0·83
haematologica | 2020; 105(7)
1973