Page 28 - Haematologica - Vol. 105 n. 6 - June 2020
P. 28
E.R.M. Scheepers et al.
Data synthesis and analysis
Due to the heterogeneity in the populations of patients and in study designs, with a wide variety in content of geriatric assess- ments, a meta-analysis was not considered feasible. We there- fore summarized the study results to describe our main out- comes of interest.
Results
Study characteristics
The literature search yielded 4,629 citations (832 from MEDLINE and 3,797 from EMBASE), of which 403 were duplicates and 4,184 were excluded for other reasons
(Online Supplementary Figure S1). This resulted in 42 eligi- ble publications from 34 studies. Cross-referencing yield- ed four additional publications. Eight publications from the 2014 review by Hamaker et al.17 were also eligible. Thus, we ultimately included 54 publications from 44 studies in this review.19-72
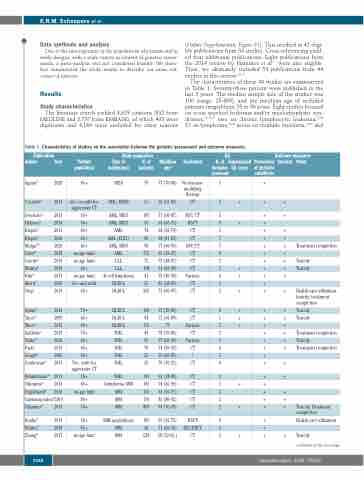
The characteristics of these 44 studies are summarized in Table 1. Seventy-three percent were published in the last 5 years. The median sample size of the studies was 100 (range, 25-869), and the me(di)an age of included patients ranged from 58 to 86 years. Eight studies focused on acute myeloid leukemia and/or myelodysplastic syn- dromes,19-25,27 two on chronic lymphocytic leukemia,28,29 13 on lymphoma,30-42 seven on multiple myeloma,42-48 and
Table 1. Characteristics of studies on the association between the geriatric assessment and outcome measures.
Publication Author Year
Aguiar19 2020
Corsetti20 2013
Patient population
65+
65+ or unfit for
aggressive CT
Study population
GA
N. of Summarized
domains GA score assessed
3
2 +
Outcome measures
Umit27 2018 Goede28 2016
Molica29 2019 Ribi30 2017 Merli31 2020
Ong32 2019
Spina33 2012 Tucci34 2009
Tucci35 2015 Aaldriks36 2015 Naito37 2016
Park38 2015 Siegel39 2006
Soubeyran40 2011
Winkelmann41 2011 Okuyama42 2015 Engelhardt43 2016
Gavriatopoulou442019
Palumbo45 2015
Rosko46 2019
Type of malignancy
MDS
AML; RAEB
N. of patients
79
31
Me(di)an age*
77 (70-84)
72 (55-84)
Treatment
No disease- modifying therapy
CT
Prevalence Survival of geriatric
conditions
+
++
Other
Deschler21 2013
Holmes22 2014 Klepin23 2013
Klepin24 2020 Molga25,26 2020
Wildes47 2019 Zhong48 2017
65+ MM 40 71(66-76) BSC;HSCT 5 noagelimit MM 628 58(52-66) CT 2 +
+
+ +
Toxicity
60+ AML; MDS 195 71 (60-87) BSC; CT
60+ AML; MDS 50 65 (60-73) HSCT 60+ AML 74 68(65-74) CT
60+ AML (FLT3) 40 68 (61-83) CT 65+ AML; MDS 98 77 (66-95) BSC;CT
no age limit AML 372 63 (19-97) CT no age limit CLL 75 75 (48-87) CT
65+ CLL 108 71(65-90) CT no age limit B-cell lymphoma 41 75 (40-94) Various
65+ and unfit DLBCL 33 82 (68-89) CT
60+ DLBCL 205 73 (60-97) CT
70+ DLBCL 100 75 (70-89) CT 65+ DLBCL 84 73 (66-89) CT
69+ DLBCL 173 77 Various 70+ NHL 44 78(70-86) CT 65+ NHL 93 77 (65-90) Various
65+ NHL 70 74(65-92) CT 60+ NHL 25 70(60-85) ?
70+, unfit for NHL 32 79 (70-92) CT aggressive CT
18+ NHL 143 63(18-88) CT
65+ Lymphoma; MM 106 74 (65-90) CT no age limit MM 125 63 (56-71) CT
80+ MM 110 83(80-92) CT
70+ MM 869 74(70-78) CT
18+ MM; amyloidosis 100 59 (36-75) HSCT
5
8+ 5
7 7
4 3
2+ 4+ 2
2+
4+ 1+
2+ 3
5
4 3
4
2 5+ 2
3
2+
6
++ + ++ ++
++ Treatment completion ++
++ Toxicity
++ Toxicity ++
+
+ +
+ +
+ + ++
+ +
+ +
+ + + ++
++ + ++ ++ + +
Health care utilization, toxicity, treatment completion
Toxicity Toxicity
Treatment completion Toxicity
Treatment completion
Toxicity, Treatment
completion
+ Health care utilization
continued on the next page
1486
haematologica | 2020; 105(6)