Page 97 - Haematologica May 2020
P. 97
Platelet vesicles and monocyte interaction
ABC
D
EF
G
H
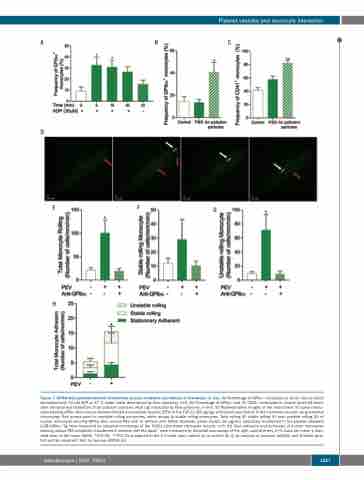
Figure 7. GPIbα from platelet-derived extracellular vesicles mediates recruitment of monocytes in vivo. (A) Percentage of GPIbα+ monocytes in whole murine blood stimulated with 30 mM ADP at 37°C under shear determined by flow cytometry, n=4. (B) Percentage of GPIbα+ and (C) CD41+ monocytes in murine blood 48 hours after intratracheal instillation of air pollution particles (400 mg) measured by flow cytometry, n=5-6. (D) Representative images of the recruitment of human mono- cytes bearing GPIbα from mouse platelet-derived extracellular vesicles (PEV) to the TGF-β1 (80 mg/kg)-stimulated vasculature in the cremaster muscle using intravital microscopy. Red arrows point to unstable rolling monocytes, white arrows to stable rolling monocytes. Total rolling (E) stable rolling (F) and unstable rolling (G) of human monocytes bearing GPIbα from mouse PEV with or without with GPIbα blockade (clone Xia.B2, 50 mg/mL) adoptively transferred in the platelet depleted IL4R/GPIbα−Τg mice measured by intravital microscopy of the TGFβ1-stimulated cremaster muscle, n=3. (H) Total adhesion and behaviors of human monocytes bearing mouse PEV adoptively transferred in western diet fed ApoE-/- mice measured by intravital microscopy of the right carotid artery, n=3. Data are mean ± stan- dard error of the mean (SEM). *P≤0.05, **P≤0.01 compared to the 0 minute (min) control (A) or control (B, C) by analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Dunnett post- test and by unpaired t-test, by two-way ANOVA (H).
haematologica | 2020; 105(5)
1257