Page 100 - Haematologica April 2020
P. 100
S. Altamura et al.
ABC
DEF
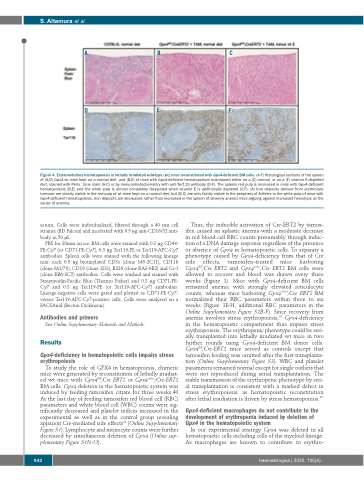
Figure 4. Extramedullary hematopoiesis in lethally irradiated wild-type (wt) mice reconstituted with Gpx4-deficient BM cells. (A-F) Histological sections of the spleen of (A,D) Gpx4 wt mice kept on a normal diet and (B,E) of mice with Gpx4-deficient hematopoiesis maintained either on a (C) normal or on a (F) vitamin E-depleted diet, stained with Perls´ blue stain (A-C) or by immunohistochemistry with anti-Ter119 antibody (D-F). The splenic red pulp is increased in mice with Gpx4-deficient hematopoiesis (B,E) and the white pulp is almost completely dissipated when vitamin E is additionally depleted (C,F). (A) Iron deposits derived from erythrocyte turnover are clearly visible in the red pulp of wt mice kept on a normal diet, but (B,C) are only faintly visible in the periphery of follicles in the white pulp of mice with Gpx4-deficient hematopoiesis. Iron deposits are decreased rather than increased in the spleen of severely anemic mice arguing against increased hemolysis as the cause of anemia.
serum. Cells were individualized, filtered through a 40 μm cell strainer (BD Falcon) and incubated with 0.5 μg anti-CD16/32 anti- body in 50 μL
PBS for 30min on ice. BM cells were stained with 0.3 μg CD44- PE-Cy7 (or CD71-PE-Cy7), 0.3 μg Ter119-PE or Ter119-APC-Cy7 antibodies. Spleen cells were stained with the following lineage mix: each 0.5 μg biotinylated CD3e (clone 145-2C11), CD11b (clone M1/70), CD19 (clone 1D3), B220 (clone RA3-6B2) and Gr-1 (clone RB6-8C5) antibodies. Cells were washed and stained with Streptavidin-Pacific Blue (Thermo Fisher) and 0.3 μg CD71-PE- Cy7 and 0.3 μg Ter119-PE (or Ter119-APC-Cy7) antibodies. Lineage-negative cells were gated and plotted as CD71-PE-Cy7- versus Ter119-APC-Cy7-positive cells. Cells were analysed on a FACSAriaI (Becton Dickinson).
Antibodies and primers
See Online Supplementary Materials and Methods. Results
Gpx4-deficiency in hematopoietic cells impairs stress erythropoiesis
To study the role of GPX4 in hematopoiesis, chimeric mice were generated by reconstitution of lethally irradiat- ed wt mice with Gpx4fl/fl;Cre ERT2 or Gpx4wt/wt;Cre-ERT2 BM cells. Gpx4 deletion in the hematopoietic system was induced by feeding tamoxifen citrate for three weeks.40 At the last day of feeding tamoxifen red blood cell (RBC) parameters and white blood cell (WBC) counts were sig- nificantly decreased and platelet indices increased in the experimental as well as in the control group revealing apparent Cre-mediated side effects33 (Online Supplementary Figure S1). Lymphocyte and monocyte counts were further decreased by simultaneous deletion of Gpx4 (Online sup- plementary Figure S1N-O).
Thus, the inducible activation of Cre-ERT2 by tamox- ifen caused an aplastic anemia with a moderate decrease in red blood cell RBC counts presumably through induc- tion of a DNA damage response regardless of the presence or absence of Gpx4 in hematopoietic cells. To separate a phenotype caused by Gpx4-deficiency from that of Cre side effects, tamoxifen-treated mice harboring Gpx4fl/fl;Cre ERT2 and Gpx4wt/wt;Cre ERT2 BM cells were allowed to recover and blood was drawn every three weeks (Figure 1). Mice with Gpx4-deficient BM cells remained anemic with strongly elevated reticulocyte counts, whereas mice harboring Gpx4wt/wt;Cre ERT2 BM normalized their RBC parameters within three to six weeks (Figure 1E-H, additional RBC parameters in the Online Supplementary Figure S2B-F). Since recovery from anemia involves stress erythropoiesis,42 Gpx4-deficiency in the hematopoietic compartment thus impairs stress erythropoiesis. The erythropenic phenotype could be seri- ally transplanted into lethally irradiated wt mice in two further rounds using Gpx4-deficient BM donor cells. Gpx4fl/fl;Cre-ERT2 mice served as controls except that tamoxifen feeding was omitted after the first transplanta- tion (Online Supplementary Figure S3). WBC and platelet parameters remained normal except for single outliers that were not reproduced during serial transplantation. The stable transmission of the erythropenic phenotype by seri- al transplantation is consistent with a marked defect in stress erythropoiesis, as hematopoietic reconstitution after lethal irradiation is driven by stress hematopoiesis.43
Gpx4-deficient macrophages do not contribute to the development of erythropenia induced by deletion of Gpx4 in the hematopoietic system
In our experimental strategy Gpx4 was deleted in all hematopoietic cells including cells of the myeloid lineage. As macrophages are known to contribute to erythro-
942
haematologica | 2020; 105(4)