Page 254 - Haematologica March 2020
P. 254
Y. Wang et al.
A
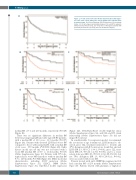
Figure 1. Overall survival (OS) after Richter transformation (RT) diagno- sis of the entire cohort and by prior chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) treatment status. (A) OS for all patients. (B) OS by previous CLL treatment status. (C) OS by temporal relationship between CLL and RT in patients with previously untreated CLL. (D) OS by lines of therapy in patients with previously treated CLL. (E) OS by prior CLL treatment category.
BC
DE
median OS of 7.1 and 12.0 months, respectively (P=0.28) (Figure 1E).
There was no significant difference in median OS between younger (age≤65) and older (age>65) RT patients, with a median OS of 13.3 versus 11.3 months (P=0.07) (Figure 2A). Patients with elevated LDH had worse OS compared to those with normal LDH, with a median OS of 6.2 versus 39.9 months (P<0.0001) (Figure 2B). Bulky disease (nodal size ≥5 cm) was not associated with a worse OS (median OS of 8.0 vs. 14.6 months; P=0.13) (Online Supplementary Figure S1). Patients with TP53 dis- ruption had a worse OS than those without (median OS 8.3 vs. 12.8 months; P=0.046) (Figure 2C). Other molecular characteristics, including IGHV mutation (Online Supplementary Figure S2), DLBCL COO (Online Supplementary Figure S3), Myc/Bcl-2 double expression
(Figure 2D), MYC/BCL2/BCL6 double-/triple-hit status (Online Supplementary Figure S4), and CLL and RT clonal relationship (Online Supplementary Figure S5) did not impact RT survival.
In a multivariable Cox regression model, we examined the association of age (continuous), LDH (normal vs. ele- vated), prior CLL treatment (untreated vs. treated) and TP53 disruption with RT survival; we found that elevated LDH (HR 2.3, 95%CI: 1.3-4.1; P=0.01), prior CLL treat- ment (HR 2.0, 95%CI: 1.2-3.5; P=0.01), and to a lesser extent older age (HR 1.03, 95%CI: 1.01-1.05; P=0.01), but not TP53 disruption (HR 1.3, 95%CI:0.8-2.1; P=0.31), were associated with worse OS.
Patients treated with an R-CHOP-like regimen (n=114) had a median OS of 15.3 months (Online Supplementary Figure S6). Patients treated with platinum or high-dose
768
haematologica | 2020; 105(3)