Page 75 - 2020_02-Haematologica-web
P. 75
Management of patients undergoing CAR T-cell therapy
different stages of their treatment course and appropriate antimicrobial prophylaxis is required. In general, centers performing allogeneic HCT will be familiar with the care of such patients and there is, as yet, no evidence that there
are infectious issues specific to CAR T-cell therapy. Table 10 summarizes recommendations for prophylaxis against the most common infections.
There is no evidence to suggest that cytomegalovirus,
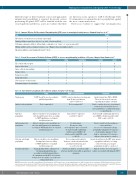
Table 8. Immune Effector Cell-Associated Encephalopathy (ICE) score to neurological toxicity assess. Adapted from Lee et al.38 Test Points
Orientation: orientation to year, month, city, hospital 4
Naming: ability to name three objects (e.g. table, television, pillow) 3 Following commands: ability to follow simple commands (e.g. “smile” or “open your mouth”) 1 Writing: ability to write a standard sentence (e.g. “Happy to have my family around”) 1 Attention: ability to count backwards from 100 by 10 1
Table 9. Cornell Assessment of Pediatric Delirium (CAPD) to assess encephalopathy in children <12 years. Adapted from Traube et al.61
Eye contact with caregiver
Purposefulactions
Aware of their surroundings Beingrestless Beinginconsolable Beingunderactive
Slow response to interactions Communicating needs and wants
always often
0 1
0 1 0 1 4 3 4 3 4 3 4 3 4 3
sometimes
2
2 2 2 2 2 2 2
rarely never
3 4
3 4 3 4 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0
Comment
Avoid if patient has CRS or ICANS There are theoretical concerns regarding macrophage activation
Can be considered in case of prolonged neutropenia and should be based on local guidelines e.g. with levofloxacin or ciprofloxacin
Start from LD conditioning until 1 year post-CAR T-cell infusion and/or until CD4+ count >0.2x109/L
Can be started later depending on center guidelines.
In case of co-trimoxazole allergy, pentamidine inhalation (300 mg once every month), dapsone 100 mg daily or atovaquone 1500 mg once daily are other agents to consider
In patients with prior allo-HCT, prior invasive aspergillosis and those receiving corticosteroids, posaconazole prophylaxis should be considered
Table 10. Anti-infective prophylaxis after chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy.
Neutropenia
Antibacterial prophylaxis
Anti-viral prophylaxis
Anti-pneumocystis prophylaxis
Systemic anti-fungal prophylaxis
IV immunoglobulins
Routine in children, consider in adults who have had infections with encapsulated organisms
Clinical evidence does not support routine use in adults following allo-HCT
Trials
G-CSF should be used according to published guidelines
Not recommended
Subjects should receive prophylaxis for infection with herpes virus, according to NCCN guidelines or standard institutional practice
Subjects should receive prophylaxis for infection with Pneumocystis pneumonia, according to NCCN guidelines or standard institutional practice
Subjects should receive prophylaxis for fungal infections according to NCCN guidelines or standard institutional practice
Gammaglobulin will be administered for hypogammaglobulinaemia according to institutional guidelines. At a minimum, trough IgG levels should be kept above 400 mg/dL, especially in the setting of infection
EBMT recommendation
G-CSF to shorten duration of neutropenia from 14 days post-infusion
can be considered
Not recommended*
Valaciclovir 500 mg bid or aciclovir 800 mg bd
Co-trimoxazole
480 mg once daily
or 960 mg three times each week To start from LD conditioning until 1 year post-CAR T-cell infusion and/or until CD4+count >0.2x109/L
Not recommended routinely; however, consider in patients with prolonged neutropenia and
on corticosteroids
EBMT: European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation; G-CSF: granulocyte colony stimulating factor; CRS: cytokine release syndrome: ICANS: immune effector cell-asso- ciated neurotoxicity syndrome; NCCN: National Comprehensive Cancer Network; LD: lymphodepleting conditioning; IV: intravenous; IgG: immunoglobulin G; allo-HCT: allogene- ic hematopoietic cell transplantation. *In patients with neutropenic fever, empiric treatment with broad spectrum antibiotics is strongly recommended.
haematologica | 2020; 105(2)
309