Page 226 - 2020_02-Haematologica-web
P. 226
A. Natoni et al.
ABCD
E
ment, we sought to investigate in vitro the effects of 3Fax-Neu5Ac pre-treatment on the sensitivity to borte- zomib in MM1SHeca452 cells in co-culture conditions that partially recapitulate the BM environment. To this end, we used the well-established HS5 stromal cell line,28 primary BM stromal cells (BMSC) derived from MM patients, and the BM endothelial cell line BMEC-60. The latter was also treated with 10 ng/mL TNFα for four hours before co-cul- ture to induce activation. BMEC-60, BMSC and, to an even greater extent, HS5 induced resistance to bortezomib (5 nM) in MM1SHeca452 cells (Figure 4A-C). 3Fax-Neu5Ac pre- treatment caused only minor, although significant re-sen- sitization to bortezomib in the presence of HS5 and BMSC (Figure 4A and B) and did not reverse BMEC-60- induced bortezomib resistance (Figure 4C). Importantly, in the absence of BM-derived cells, the 3Fax-Neu5Ac pre- treatment had only a minor effect on the MM1SHeca452 response to bortezomib. Together these data indicate that, in MM cells, bortezomib resistance that is BM stromal cell-driven, although maybe not endothelial cell-driven, can be partially reversed by inhibition of sialylation.
3Fax-Neu5Ac treatment does not affect migration in response to SDF1α
Since 3Fax-Neu5Ac did not completely reverse borte- zomib resistance induced by BM cell lines and patient- derived-BMSC in vitro, we reasoned that the mechanism(s) of bortezomib re-sensitization in vivo induced by 3Fax-Neu5Ac may also involve a defect in the ability of the MM1SHeca452 cells to home into the protective BM microen- vironment. To explore this possibility, we first examined the effects of 3Fax-Neu5Ac pre-treatment on migration in
response to SDF1α in a transwell assay. DMSO and 3Fax-Neu5Ac pre-treated MM1SHeca452 cells showed enhanced migration in response to SDF1α (Figure 5A). However, spontaneous as well as SDF1α-induced migra- tion were similarly inhibited by 3Fax-Neu5Ac pre-treat- ment (Figure 5A). Indeed, when we specifically examined migration in response to SDF1α by subtracting sponta- neous migration (no SDF1α) to SDF1α-containing sam- ples, we observed that 3Fax-Neu5Ac pre-treatment did not affect SDF1α-driven migration (Figure 5B). These data suggest that 3Fax-Neu5Ac pre-treatment has an impact on the motility of the cells but not specifically on SDF1α- induced migration.
3Fax-Neu5Ac treatment impairs adhesion and rolling of MM1SHeca452 cells on E-selectin, MADCAM1 and VCAM1
We next examined whether 3Fax-Neu5Ac could influ- ence adhesion and rolling on selectins and integrin co- receptors important in BM homing.3-5 To this end, we per- formed adhesion and rolling assays under shear stress on E-selectin, MADCAM1 and VCAM1-coated substrates. MM1SHeca452 cells showed robust interactions with E-selectin which could be subcategorized into firm adhe- sion and rolling (Figure 6A-C).3Fax-Neu5Ac pre-treatment dramatically impaired this interaction by decreasing the number of adherent cells (Figure 6A and C). The number of rolling cells was not affected (Figure 6B). However, when we looked at the rolling velocity, we observed an increase in the velocity of the MM1SHeca452 cells pre-treated with 3Fax-Neu5Ac versus DMSO controls, indicating a decrease in the affinity of the E-selectin ligands for E- selectin (Online Supplementary Figure S4A-C). These data
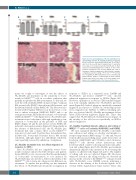
Figure 1. Decreased sialylation of B cells and kidney toxi- city following systemic 3Fax-Neu5Ac treatment. Peripheral blood B cells were stained with SNA (A and B) or PNA (C and D) on the seventh day of dosing (A and C) and after seven days of recovery post last injection (B and D). Bars represent mean±Standard Error of Mean of three inde- pendent experiments. The one-way ANOVA was used to determine statistical significance with Dunnett’s multiple comparison post-hoc testing. **P<0.01; ****P<0.0001; ns: non-significant. MFI: median fluorescence intensity. (E) Representative images of Hematoxylin & Eosin stained kidneys taken after seven days of recovery. Images were taken at 20x magnification of four representative mice.
460
haematologica | 2020; 105(2)