Page 233 - Haematologica Atlas of Hematologic Cytology
P. 233
CHAPTER 27 - Acquired hemolytic anemias
AB
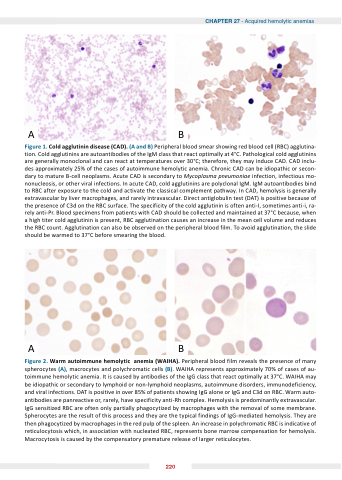
Figure 1 old old old agglutinin agglutinin agglutinin disease ( ( ( D) ( ( ( and ) ) ) Peripheral blood blood smear showing red blood blood cell (RBC) agglutina- tion Cold agglutinins agglutinins are are autoantibodies of the the the IgM class that react react optimally at at at at at 4°C Pathological cold agglutinins agglutinins are are generally monoclonal and can can react react at at at at at at at temperatures over 30°C therefore they may induce CAD CAD CAD CAD CAD CAD inclu- des approximately 25% of of the the the cases of of autoimmune hemolytic anemia Chronic CAD CAD CAD CAD can can be idiopathic or or secon- dary dary to to to to mature B-cell neoplasms Acute CAD CAD CAD is is secondary to to to to Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection infection infectious mo- nonucleosis or other viral infections In In acute CAD CAD CAD cold cold agglutinins are polyclonal IgM IgM IgM IgM autoantibodies bind to to to RBC after exposure to to to the the the cold cold and and activate the the the classical complement pathway In In CAD CAD hemolysis is is is is generally extravascular by liver macrophages and and rarely intravascular Direct antiglobulin test (DAT) is is is is positive because of of of of the the the presence of of of of C3d on the the the RBC surface The specificity of of of of the the the cold agglutinin is is often anti-I sometimes anti-i ra- rely anti-Pr Blood specimens from patients with CAD should be be collected and and maintained at at at 37°C because when a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a high titer cold agglutinin is present RBC RBC agglutination agglutination causes an an an an an an increase in in in in in in in in in the the the the mean cell volume and and reduces the the the the the RBC RBC count Agglutination can also be be be observed on on on on the the the the the peripheral blood blood film To avoid agglutination agglutination the the the the the slide should be be be warmed to 37°C before smearing the the the blood AB
Figure arm autoimmune hemolytic anemia ( IH ) Peripheral blood film reveals the presence of many spherocytes (A) macrocytes and polychromatic cells (B) WAIHA represents approximately 70% of of cases of of au- toimmune hemolytic anemia It is caused by antibodies of the IgG class that react optimally at at 37°C WAIHA may be idiopathic or or or secondary to to lymphoid lymphoid or or or non-lymphoid neoplasms autoimmune disorders immunodeficiency and and viral infections DAT is positive in in in over 85% of patients showing IgG IgG alone or IgG IgG and and C3d on on on RBC Warm auto- antibodies are are panreactive or rarely have specificity anti-Rh complex Hemolysis is is predominantly extravascular IgG sensitized RBC are often only partially phagocytized by macrophages with the removal of of some membrane Spherocytes are are are the the the result of of this process and they are are are the the the typical findings of of IgG-mediated hemolysis They are are are then phagocytized by macrophages in in in in the the the red pulp of of the the the spleen An increase in in in in polychromatic RBC is indicative of of reticulocytosis which in association with nucleated RBC represents bone marrow compensation for hemolysis Macrocytosis is is caused by the compensatory premature release of larger reticulocytes 220