Page 207 - 2019_09-HaematologicaMondo-web
P. 207
Redox-dependent regulation of platelets
NOX2 ablation (Online Supplementary Figure S11). As these modulators induce little or no aggregation on their own, we analyzed the modulatory effect of oxLDL and Aβ1-42 in aggregation experiments using NOX1-/- and NOX2-/- mouse platelets. We showed that oxLDL (Figure 8B) and Aβ1-42
(Figure 8D) potentiate the aggregation induced by collagen in wild-type mice but not in NOX2-/- mice, and the aggrega- tion stimulated by thrombin in wild-type mice but not in NOX1-/- mice. The potentiation of collagen response could not be tested in NOX1-/- mice, which do not respond to this
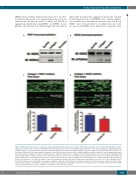
AB
CD
Figure 4. NOX1 is the main source of superoxide anions in human platelet response to collagen, while NOX2 is the main source of thrombin-dependent reactive oxygen species (ROS). The activation of NOX1 (A) and NOX2 (B) was assessed by co-immunoprecipitation with their canonical activating and organizing subunits NOXA1 and p47phox, respectively. 400 μL of platelet suspension (4x108 platelets/mL) were stimulated with 10 μg/mL collagen or 0.1 unit/mL thrombin or vehicle solu- tion (Tyrode’s buffer) for 10 minutes (min) before gentle cell lysis (NP40 buffer). Specific NOX1 or NOX2 antibodies and Protein A/G were used to immunoprecipitate the NOX complexes (which by extension should include their regulatory subunits after activation). The immunoprecipitates were tested by immunoblotting using NOX1, NOXA1, NOX2 or p47phox antibodies (as indicated). The data are representative of 4 independent experiments. The functional role of NOX1 and NOX2 in col- lagen-dependent platelet activation was assessed in a whole blood flow assay (C and D). Platelets were stained with DiOC6 as described and the Bioflux platform (Fluxion, San Francisco, CA, USA) was utilized to assess the thrombus formation induced by collagen under physiological flow (1000 sec-1). The experiments were performed in the presence of NoxA1ds or its negative scrambled control (C) or Nox2ds-tat or its negative scrambled control (D). Images were taken at 10 min of flow and are representative of 4 independent experiments. They were quantified by assessing the surface area coverage by platelets (C and D, bottom). Statistical signif- icance was tested by t-test. *P<0.05 compared to scrambled control. N=4 for (C and D).
haematologica | 2019; 104(9)
1885