Page 172 - 2019_09-HaematologicaMondo-web
P. 172
S.C. Oostindie et al.
(P<0.05) (Online Supplementary Figure S3A and B). Importantly, significantly increased CDC levels were observed in 9 of 15 tested CLL donors upon treatment with the combination of Hx-CD20-7D8 and Hx-CD37. Even at modest total concentrations of Hx-CD20-7D8 and Hx-CD37 (≤1.25 μg/mL for each mAb), >90% CDC of B cells was induced in 12 of the 15 tested CLL donors (Figure 6A). Enhanced CDC by the mAb combination was observed over a range of mAb concentrations and at dif- ferent mAb ratios, and was more apparent at lower mAb concentrations, as illustrated for one representative donor (Figure 6B). Next, we evaluated the cytotoxic capacity of Hx-CD20-11B8, Hx-CD37, and the combination thereof using tumor cells of ten patients diagnosed with different B-cell lymphomas, including B-cell non-Hodgkin lym- phoma (B-NHL) not otherwise specified (NOS), follicular lymphoma (FL), marginal zone lymphomas (MZL) and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL). While for the single agents a large variation in CDC efficacy was observed between the donors, the combination of Hx-CD20-11B8 and Hx-CD37 consistently showed enhanced CDC activity
compared to the individual mAbs (Figure 6C). Representative figures from each tested lymphoma sub- type show that combinations of Hx-CD20-11B8 and Hx-CD37 at the tested 1:1 ratio may enhance CDC, even when CDC induced by the individual mAbs was low or absent (Figure 6D). Furthermore, analysis of CD20 and CD37 target expression levels on primary B cells from 24 CLL patients and ten patients with different NHL sub- types illustrated a large diversity in target expression levels and ratios (Online Supplementary Figure S3A-C). These results suggest that combinations of Hx-CD20 and Hx- CD37 mAbs may generally increase the therapeutic potential of CDC-inducing mAbs in B-cell malignancies across different target expression levels and ratios.
Discussion
Improving therapeutic efficacy against (heterogeneous) tumors has been the focus of intense preclinical and clinical development. We previously showed that the therapeutic
A
B
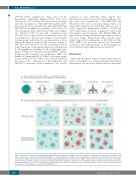
Figure 7. Model for Fc-mediated clustering of CD20 and CD37 monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) in hetero-hexamers upon binding to the cell surface. (A) mAbs naturally cluster into hexameric complexes upon antibody binding to a cognate antigen on a target cell, thereby providing a docking site for C1q binding and complement- dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) induction. (B) Upon binding of mAbs targeting two different coexpressed antigens on the plasma membrane that (are able to) colocalize, hetero-hexameric antibody complexes are formed consisting of both mAbs, providing a docking site for C1q binding and CDC induction. Introducing hexamerization- enhancing mutations can increase Fc-mediated clustering of mAbs, both into homo- and hetero-hexameric antibody complexes on the cell surface, thereby increasing the number of C1q docking sites and further potentiating CDC.
1850
haematologica | 2019; 104(9)