Page 119 - 2019_08-Haematologica-web
P. 119
Oncogenic mechanisms of ZEB1 and LM02 in T-ALL
After 4 weeks of culture, a large proportion of the R26- Zeb2tg/+ cells remained DN3 with intermediate levels of CD25, whereas all T cells had already differentiated beyond the DN stage in the control cultures (Figure 2B).
Zeb2-mediated increased interleukin-7 receptor signaling is involved in the T-cell differentiation delay
In our previous study, we demonstrated that ZEB2 direct- ly regulates the Il7r promoter.33 Consequently, Zeb2-overex- pressing T-ALL tumors and derived cell lines have high lev- els of Il7r mRNA and are more responsive to exogenous IL7
A
levels. As downregulation of IL7 signaling, induced by the pre-TCR signal, is crucial for normal transition of DN3 to double-positive cells,34,35 we hypothesized that the Zeb2- induced delay in T-cell differentiation is due to their inabil- ity to downregulate Il7r. We therefore tested whether low- ering the amount of recombinant IL7 in the culture medium could overcome the observed delay in T-cell differentiation in vitro. Indeed, reduction of the concentration of recombi- nant IL7 from 5 ng/mL to 0.2 ng/mL rescued the delay in differentiation, resulting in similar developmental kinetics to that of the control co-cultures (Figure 2C).
BC
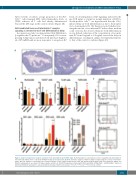
Figure 1. Zeb2 overexpression results in a delay in T-cell development at the DN3 stage. (A) Hematoxylin & eosin-stained sections of paraffin-embedded thymi of mice with and without mono- or bi-allelic ROSA26-mediated overexpression. (B) Flow cytometric analysis of thymi of Zeb2-overexpressing mice versus control litter- mates. Absolute numbers of total thymocytes and percentages of CD3, CD4/8 double-positive (DP) and CD4/8 double-negative (DN) cell populations, DN1-4 and DN3A-C subpopulations are shown. (C) Representative dot plots of CD4/8 DN populations stained with CD25 and CD44. In R26-Zeb2tg/+ and R26-Zeb2tg/tg thymi, an abnormal DN3/4-like population is observed with intermediate CD25 levels (arrows). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 (vs control).
haematologica | 2019; 104(8)
1611