Page 49 - 2019_07 resto del Mondo-web
P. 49
RSV in HCT and hematologic malignancies
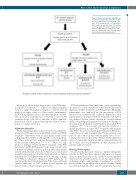
Figure 1. Proposed treatment algorithm for respiratory syncytial virus infections in allo- geneic hematopoietic cell transplant recipi- ents. HCT: hematopoietic cell transplant; RSV: respiratory syncytial virus; CT: comput- ed tomography; LRTI: lower respiratory tract infection; URTI: upper respiratory tract infec- tion; ISI: Immunodeficiency Scoring Index; IVIG: intravenous immunoglobulins.
Intravenous ribavirin has been used to treat RSV infec- tion in HCT recipients.24,45,49,80 The most common regimen used is a single 33 mg/kg loading dose, followed by 16 mg/kg four times a day for 4 days with a maintenance dose of 8 mg/kg three times a day until symptoms resolve. The intravenous formulation of ribavirin is not readily available in the USA due to the lack of FDA approval; however, it can be acquired through the FDA for emer- gency or compassionate use.
Adjunctive therapies
Many immunomodulators have been used as adjunctive therapy for RSV infections in adult HM patients and HCT recipients. There have been no randomized control trials comparing the benefits of adding IVIG to ribavirin thera- py. Many retrospective analyses have reported variable results for this combination.22,42,45,46,49,53,85,93,94 Shah et al. sug- gested a minimal benefit in HCT recipients with RSV infections;42 all 51 HCT patients who were treated with combination therapy survived, and only one of 61 patients treated with ribavirin alone died. This was not evaluated in multivariate analysis. Another study showed no clinical benefit in HCT recipients who received weekly or high- dose IVIG as adjunctive therapy for RSV infections.46 It was hypothesized that humanized IVIG lacks sufficient specific antibodies to RSV, which would explain the mixed results seen in retrospective studies.
RSV-specific monoclonal antibodies, such as palivizum- ab, have also been evaluated for the treatment of RSV infections in HCT recipients and HM patients. Originally, palivizumab was approved for the prevention of RSV infections in neonates and children. Experience with palivizumab as treatment in HCT recipients with RSV is very limited. Several studies showed no survival benefit when comparing palivizumab as adjunctive therapy to ribavirin as monotherapy for RSV infections in adult HCT recipients.42,46,83,95,96 In a recent retrospective study of a mixed population of adult HCT recipients and patients with HM,97 those treated with palivizumab for RSV infec- tions showed a trend towards better 90-day survival com- pared to the control group, with mortality rates of 11% compared to 17%, respectively.97 However, this difference was not statistically significant and recommendations for the routine use of palivizumab in this population of patients cannot be made.
Investigational agents
As previously discussed, there are limited therapeutic options for RSV infections and new therapies are desper- ately needed. Presatovir is an oral RSV fusion inhibitor with selective anti-RSV activity in vitro. In a phase I, first- in-human, single- and multiple-ascending dose study,98 presatovir had an excellent safety profile, despite having an extended half-life. The oral bioavailability was also
haematologica | 2019; 104(7)
1327