Page 33 - 2019_07 resto del Mondo-web
P. 33
In vivo manipulation of Treg cells
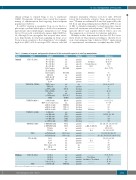
clinical settings to expand Tregs in vivo to ameliorate GvHD. Therapeutic strategies have varied the reagents, timing of administration and targeting donor/recipient populations (Table 1).
IL-2/CD25 targeting to manipulate Tregs in vivo. IL-2 is a pleiotropic cytokine which plays a dual role in maintain- ing tolerance and contributing to immunity in vivo.35 Tregs but not Tconv cells constitutively express high CD25 lev- els, although Tconv up-regulate this receptor after activa- tion. Importantly, downstream signaling in Tregs versus Tconv is more sensitive to IL-2 stimulation.36 Accordingly, high doses (HD) of IL-2 can target CD4+ effector cells and
stimulate immunity whereas low-dose (LD; 100-fold lower) IL-2 selectively activates Tregs, promoting toler- ance.36 Human recombinant IL-2 was first approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1998 for use at HD to stimulate immunity toward metastatic cancers (renal cell carcinoma and melanoma).37 LD IL-2 has mini- mal side effects38 and, together with its effects on in vivo Treg expansion, is of interest for tolerance induction.
Multiple studies demonstrated that free LD IL-2 treat- ment results in Treg expansion leading to efficient rever- sion of autoimmune type 1 diabetes (T1D),39 amelioration of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE)40
Table 1. Summary of reagents and properties discussed in this review with regard to in vivo Treg manipulation.
Study
Animal
Target
CD25 (IL-2Ra)
TNFRSF1B (TNFR2)
TNFRSF4 (OX-40)
TNFRSF9 (4-1BB)
TNFRSF25 (DR3)
CD28
ST2 (IL-33R)
CD25 (IL-2Ra) CD28
Reagent
Free LD IL-2 Free LD IL-2 Free LD IL-2 Free LD IL-2 IL-2 Complex (IL-2/anti-IL2) IL-2 Complex AAV-IL-2 CD25-IL-2 FP IgG-IL-2 FP IL-233
Clone
n/a n/a n/a n/a JES-1A12
JES-1A12 n/a n/a n/a
n/a
n/a XT3.11 n/a n/a TR75-54.7 TNFR2
OX-86 n/a RM134L KY1005 KY1005
n/a 3H3 158321 1AH2 TKS1
4C12 4C12 n/a n/a
D665 (ms)
JJ316 (rat)
n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a
n/a n/a n/a n/a TGN1412
Property
agonistic agonistic agnostic agnostic agonistic
agonistic agonistic agonistic agonistic agonistic
n/a agonistic blocking agonistic agonistic blocking agonistic
agonistic agonistic blocking blocking blocking
agonistic agonistic agonistic agonistic blocking
agonistic agonistic agonistic agonistic
agonistic
agonistic
agonistic agonistic agonistic n/a
n/a
n/a
agonistic agonistic agonistic agonistic agonistic
Combinations
----------- Sirolimus Dexamethasone IL-33 ------------
Sirolimus ------------ ------------ ------------ ------------
------------
------------ ------------ ------------ ------------ ------------
------------ ------------ ------------ ------------ Sirolimus
------------ ------------ ------------ ------------ ------------
------------ a-OX-40 (OX-86) ------------ IL-2
------------
------------
------------ IL-2 ------------ ------------ ------------ ------------
------------ Tacrolimus Sirolimus + Tacrolimus ------------ ------------
References
39-41, 79 42, 43, 80 44, 83 56 45-50, 77,78
51 52, 53 54 55 56
TNFR-/- mice TNFR2-Fc a-TNF-a mAb TNC-scTNF80 TNF-a a-TNFR2 mAb STAR2
88, 89,
92, 93, 97 90
91
a-OX-40 mAb OX-40-L overexpression a-OX-40-L mAb a-OX-40-L mAb a-OX-40-L mAb
94, 95 96 97 98
100-107, 109 100-104 108
110
110
113 114-116, 120, 121 117
118
119
126, 127, 130, 131, 133, 135 128, 129 127,130,133
130, 132, 136,137
139, 142, 146, 148, 153
140, 141, 143-145,147, 149,150-152
158, 159, 161-165 56
56
167
167
167
70-73, 75, 76 75
81, 82 74, 84 154
4-1BB-L-Fc a-4-1BB mAb a-4-1BB mAb a-4-1BB mAb a-4-1BB-L mAb
a-TNFRSF25 mAb a-TNFRSF25 mAb TL1A-Ig TL1A-Ig
a-CD28SA mAb a-CD28SA mAb
Human
IL-33
IL-33 IL-233 ST2-/- donor cells ST2-Fc IL-33-/- recipients
LD IL-2 LD IL-2 LD IL-2 Ultra LD IL-2 a-CD28 mAb
LD: low dose; HD: high dose: n/a: not applicable.
haematologica | 2019; 104(7)
1311