Page 135 - 2019_07 resto del Mondo-web
P. 135
ERG deletion in BCP-ALL
formed random down-sampling of total reads to 5x104. ERGdel was reliably detected (supported by > 150 reads) in all AmpliSeq-positive patients except for Patient UPN- 004, where only four ERGdel reads were found after down-sampling.
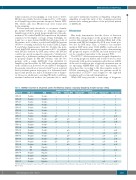
We have previously described a co-occurrence of multi- ple distinct ERGdel subclones at leukemia diagnosis.3 AmpliSeq provided a much deeper insight into this phe- nomenon. We studied IntERGdel repertoire in 24 patients sequenced at the higher coverage setting. Strikingly, we found two or more distinct IntERGdel subclones in 22 of 24 patients; in 14 of these, a polyclonal IntERGdel pattern (10-50 co-occurring subclones) was found (Table 2, Figure 5, and Online Supplementary Table S3). Notably, the poly- clonal IntERGdel pattern was present in 50% of patients with ERGdel detected by SNP array, where the ERGdel could be incorrectly assumed to represent a “clonal lesion” acquired by a leukemia-founding cell and inherited by all its progeny (Figure 6). On the contrary, only the two patients with a single IntERGdel clone identified by AmpliSeq (and detectable by SNP array) might represent such a clonal lesion; however, we are unable to distinguish the genuine clonal from a “pseudoclonal” lesion, acquired later in leukemogenesis in progeny of a leukemia-found- ing cell and present in a major, dominant clone at diagno- sis. Moreover, additional co-existing ERGdel(s) could have remained undetected in these two patients due to small
size and/or inefficient sensitivity of AmpliSeq. Altogether, AmpliSeq revealed the rarity of the clonal/pseudoclonal pattern and a striking prevalence of the polyclonal pattern of IntERGdel.
Discussion
Our study demonstrates that the choice of detection method has a huge impact on the proportion of ERGdel- positive ALL patients that are identified. Only half of the patients with ERGdel identified by PCR were found posi- tive also by SNP array. Thus, a switch to less sensitive methods (SNP array, array CGH, MLPA) could result in a significant deviation from original studies demonstrating the prognostic impact of ERGdel and such methods can- not be considered equivalent to the genomic PCR.
The IKZF1plus deletion pattern was recently identified to be a strong prognostic marker and it will be used to strat- ify patients with positive minimal residual disease (MRD) at the end of induction into a high-risk treatment arm on an upcoming AIEOP-BFM ALL trial.4 Importantly, we show here that, according to the false negative results of ERGdel screening by SNP array, five patients would be misclassified as IKZF1plus and assigned to the high-risk treatment and/or stem cell transplantation.
While SNP array provides a wide range of diagnostic
Table 2. IntERGdel repertoire in 24 patients positive for ERGdel by amplicon sequencing (AmpliSeq) at higher coverage setting. Number of IntERGdel clones detected by AmpliSeq‡
Patient ID
UPN-011
UPN-047 UPN-103 UPN-099 UPN-025 UPN-083 UPN-009 UPN-007 UPN-019 UPN-078 UPN-002 UPN-048 UPN-072 UPN-008 UPN-061 UPN-068 UPN-013 UPN-014 UPN-018 UPN-051 UPN-004 UPN-023 UPN-055
UPN-037
SNP array
Positive
Positive Positive Positive Positive Positive Positive Positive Positive Positive* Negative Negative Negative Negative Negative Negative Negative Negative ND
ND
Negative
Negative
Negative
Negative
PCR
Positive
Positive
Positive
Positive
Positive
Positive
Positive
Positive
Positive
Positive
Positive
Positive
Positive
Positive
Positive
Positive
Positive
Positive
Negative
Negative
Negative
Negative
Negative
Negative
Utilizing BP1 Utilizing BP2 Utilizing BP3 Utilizing BP4 Utilizing BP5
-1- -- 1-- -
Total number‡
1
1 4 5 9 11 17 ≥33 ≥43 ≥44 4
10 ≥28 ≥29 ≥33 ≥46 ≥48 ≥49
11 1 -- 1 - 11 2 1 35 2 -
1 4 4 1 8 7 ≥10 ≥10 2
2
1 ≥10 ≥10 ≥10 - 3 7 6 9 ≥10 ≥10 9
3 3 2
6 8 2 ≥10 ≥10 3 ≥10 ≥10 4
1 1 -
3 1 1 ≥10 6 1 2 ≥10 1 ≥10 4 - ≥10 ≥10 6 ≥10 ≥10 8
4 ≥10 ≥10 ≥10 ≥10 ≥10
≥10 ≥10 ≥10
1 - 2 - 6 9
6 8 9 5
≥10 ≥38
---- 11-- 115- 2111
2 2
2 4
1 8
≥10 ≥15
*ERGdel-diff. ‡From manually curated data. SNP: single nueclotide polymorphism; PCR: polymerase chain reaction; BP: breakpoint site cluster; UPN: unique patient number; ND: not done.
haematologica | 2019; 104(7)
1413