Page 40 - 2018_11-Haematologica-web
P. 40
J. Caers et al.
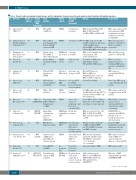
Table 5. Recent studies on minimal residual disease and the implications for progression-free and overall survival of patients with multiple myeloma.
N. Reference
#1 Lahuerta et al., JCO 2017.105
#2 Chakraborty et al., Biol Blood Marrow
Transplant 2017.106
#3 Nadiminti et al., OncoTargets and
Therapy 2017.107
#4 Paiva et al.; Blood 2016.108
#5 Ludwig et al.; BJH 2015.109
#6 Roussel et al.; JCO 2014.110
#7 Mateos et al.; Blood 2014.111
#8 Oliva et al., Oncotarget 2017.112
#9 Puig et al.; Leukemia 2014.113
#10 Ferrero et al.; Leukemia 2015.114
#11 Martinez-Lopez
et al.; Blood 2014.90
#12 Chari et al.; Blood 2017.115
#13 Korde et al.;
JAMA Oncol. 2015.116
Number of patients
609
185
100
162
93
31
260
50
170
39
133
103
45
Method used for MRD assessment
MFC
MFC
MFC
MFC
MFC
MFC
MFC
MFC and ASO-RQ-PCR
ASO RQ- PCR; MFC
PCR
MFC and NGS
NGS
MFC, NGS, FGD-PET/CT
Study question
PFS and OS in MRD– pts
PFS and OS in post-transplant sCR patients with HR cytogenetic MM
Toxicity, safety, PFS and OS of
VTD + HD melphalan
Monitor MRD in transplant-ineligible pts
VTD and VTCD induction in NDMM
VRD induction and consolidation for ASCT pts
VMP vs. VTP as induction
Consolidation with ASCT or CRD plus R maintenance
→ MRD
Applicability, sensitivity and prognostic value of
ASO RQ-PCR
MRD kinetics’ impact on survival
Prognostic value of MRD in pts with VGPR after front-line therapy
Safety, OS/PFS and MRD
Tolerability and impact on MRD
negativity
Patient cohorts
NDMM
NDMM
NDMM and pre-treated
NDMM elderly
Untreated MM, elderly
Untreated MM,
<65 years
NMDD, >65 years
NDMM
NDMM with and without
ASCT
NDMM with ASCT
NDMM
≥2 treatment lines
NDMM and HR SMM
Time point of MRD assessment
9 months after treatment
3 months post-ASCT
6 months post-ASCT
At ID after 9,18 cycles
At baseline and at suspected CR
ID + pre-ASCT, post-ASCT, post-consolidation, end of treatment
6 cycles of induction
After 3 and 6 courses of maintenance and then every
6 months till PD
ID and after treatment
ID, study entry, after 2 cycles
CTD, end of treatment, every 6 months until PD
After induction for elderly, after ASCT for
<65 years
PtsinCRor better after treatment
ID, achievement of CR and/or completion of cycles 8, 20 and 32, end of treatment
Results
MRD– prolonged PFS and OS; MRD+ in CR similar PFS
and OS to MRD+ in nCR and PR.
56% MRD– with superior OS
and PFS; del17 pts no difference
in PFS and OS between
sCR and MRD–; t(4;14) pts superior PFS and OS in MRD– pts than sCR
MRD– in 85% 6 months after transplantation, sCR in56%andCRin20%
Determines 3 MRD groups, with significant longer
PFS and OS for MRD– group
OS and PFS longer in
MRD– vs. MRD+ pts
with BM CR. Same results for MRD– in VGPR or PR group
58% in CR, 68% MRD–.
22% MRD– with longer PFS
and OS. VMP better than VTP. 70% in CR after VMP also MRD– only 45% in VTP group.
Lower MRD in ASCT vs. CRD pts. Differences between HR vs. SR and relapse vs. non-relapse pts
MRD assessed in 103 pts.; 54% MRD+ by PCR, 46% by MFC. MRD– pts had prolonged PFS
and OS
OS 72% at 8 years median FU in MRD– and 48% in MRD+
pts. PFS for MRD– 38 months and MRD+ 9 months
MRD– pts had significantly longer PFS and OS; median PFS: MRD≥10-3 27 months, 10-3-10-5 48 months;
<10-5 80 months.
29% of pts in CR are MRD–;
nCR or better pts were MRD– in 100% NDMM /92% SMM by MFC, 67%/75% by NGS and 41%/26% by FGD-PET/CT
Lesson learnt
MRD– status surpasses CR in all risk groups. MRD negativity most relevant endpoint for elderly fit pts with ASCT.
MRD status important markers for survival but differs according to cytogenetics
MRD and sCR excellent markers for PFS and OS
MRD is a relevant prognostic factor in elderly and MRD status correlates with OS and PFS
MRD surpasses conventional SFLC and BM CR
None of the MRD– group relapsed during a FU of 39
months
MRD surpasses CR and is a prognostic factor for OS and PFS
MRD identifies a low-risk group, response independently, better characterizes activity
of treatment.
ASO RQ-PCR less applicable than MFC but powerful to assess treatment efficacy and risk stratification
Long-term MRD monitoring is useful and maintenance therapy ensures responses
MRD surpasses CR and depth of MRD level showed significant
differences in pts with CR
MRD surpasses CR
High rates of MRD negativity with longer PFS in NDMM/HR SMM
continued on the next page
1780
haematologica | 2018; 103(11)