Page 183 - 2018_10-Haematologica-web
P. 183
Platelet activation by HLA antibodies
platelet transfusions and containing HLA antibodies, were capable of activating platelets (Online Supplementary Table S1). Thirteen sera were tested with platelets from two donors. In each serum HLA antibodies matching the HLA type of the donor platelets were present. Addition of con- trol serum lacking HLA antibodies induced low levels of activation in both experiments (Figure 5A,C). Four of the 13 sera induced CD62P exposure on platelets from donor 1. Activation of platelets could be inhibited by IV.3 and Syk inhibitor to background levels as observed for platelets incubated with control serum (Figure 5A,B). When tested with platelets from donor 2, pronounced activation was observed for sera 1, 3, 7, 12 and 13 (Figure 5C,D). Sera 1, 12 and 13 were capable of activating platelets of both donor 1 and 2; serum 8 exclusively acti- vated platelets of donor 1 and sera 3 and 7 only activated platelets from donor 2. Levels of IgG binding were rela- tively higher for sera which induced enhanced CD62P exposure, although some sera induced significant activa- tion despite relatively low levels of IgG binding. Together,
AB
these results suggest that HLA antibodies in sera from refractory patients can induce FcγRIIa-dependent platelet activation.
HLA monoclonal antibodies induce phagocytosis by macrophages
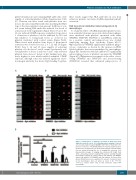
To study the effect of FcγRIIa-dependent platelet activa- tion on platelet clearance, monocyte-derived macrophages were incubated with platelets opsonized with either WIM8E5, SN607D8, SN230G6 or anti-HPA-1a antibody (as a positive control) and phagocytosis was studied employing imaging flow cytometry (Figure 6A-C). Opsonization by WIM8E5 significantly enhanced phago- cytosis of platelets as shown by the increase in PKH- labeled platelets that were internalized by macrophages (Figure 6B). Incubation with Syk inhibitor IV significantly reduced phagocytosis of platelets opsonized by WIM8E5 (Figure 6C). Quantitative assessment of the effect of acti- vating (WIM8E5 and SN607D8) and non-activating (SN230G6) revealed that enhanced phagocytosis of
D
C
Figure 6. Phagocytosis of platelets opsonized by HLA monoclonal antibodies and the effect of FcγRIIa-dependent signaling. Platelets were incubated with 10 mg/mL WIM8E5, SN607D8 or SN230G6 in the presence or absence of 5 mM Syk inhibitor IV. Opsonized platelets were incubated for 1 h with monocyte-derived macrophages and internaliza- tion was analyzed through the use of imaging flow cytometry. (A-C) Representative images of imaging flow cytometry. BF: bright field; CD61: extracellular platelet staining; PKH: platelet staining; HLA-DR: macrophage staining. (A) Control without Syk inhibitor, (B) WIM8E5 without Syk inhibitor, (C) WIM8E5 with Syk inhibitor. (D) Intracellular platelet (PKH) fluorescence quantifies the amount of platelets taken up by macrophages. Data are given as mean ± SD, *P<0.05, **P<0.01. Control: buffer only, no HLA antibodies added. MF: macrophage.
haematologica | 2018; 103(10)
1749