Page 84 - Haematologica July
P. 84
1162
C.H.S. Lin et al.
AB
C
D
E
FG
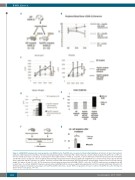
Figure 1. JAK2V617F hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells (HSPCs) in the Tie2/FF1 mice are protected from lethal irradiation. (A) Scheme of direct marrow trans- plantation. (B) Peripheral blood CD45.1 chimerism following transplantation of wild-type (WT) CD45.1 marrow cells into lethally irradiated Tie2/FF1 mice or WT con- trol mice (CD45.2) (n=12 in each group). (C) During more than eight months of follow up, Tie2/FF1 recipients with mixed chimerism developed both neutrophilia and thrombocytosis. (D) Spleens collected eight months following transplantation did not display significant weight differences between Tie2/FF1 recipients with full donor chimerism and WT recipients. In contrast, Tie2/FF1 recipients with mixed chimerism developed moderate splenomegaly compared to WT recipients (spleen weight 196 mg vs. 80 mg; P=0.010). (E) The frequency of normal marrow donor-derived E-SLAM (CD45.1) cells in the Tie2/FF1 recipients was unchanged from WT recipient mice. In contrast, JAK2V617F-mutant recipient-derived E-SLAM (CD45.2) cells were significantly expanded in Tie2/FF1 recipients with mixed chimerism. (F) Schematic diagram of irradiation and analysis of Tie2/FF1 and WT control mice. (G) Lin– HSPC cell apoptosis in Tie2-cre control or Tie2/FF1 mice after 300cGy irra- diation (n=2 in each group). *P<0.05.
haematologica | 2018; 103(7)