Page 69 - Haematologica July
P. 69
Late effects after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for thalassemia major
planted early in childhood from MSD and all received mye- loablative conditioning regimen (MAC), most often BuCy.
At last evaluation, hypogonadism, defined as low estradi- ol levels or need for long-term sex hormone replacement therapy, was observed in 58% of female patients. Hypogonadism was hypergonadotropic in 84% of cases, the few cases of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism being observed in female patients who were post-pubertal or over 13 years at transplant. After transplant for thalassemia, ovarian failure has been reported with a frequency ranging from 50% to 100% (Table 4).18-25 Here, we report that gonadal dysfunction generally resulted from the busulfan- related ovarian toxicity rather than IO which would lead to
hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. In several studies of β- TM patients, older age at HSCT (>7 years) has been associ- ated with more frequent post-transplant hypogo- nadism.14,20,22,24,25 This observation can be explained by the fact that the older the patient at HSCT, the higher the pre- transplant exposure to IO, but also by a possible reduced gonadal toxicity to busulfan in very young children. The pool of oocytes is limited and decreases from birth,26 and pre-pubertal gonadal quiescence is gonadal-protective in children receiving chemotherapy.27 High-dose busulfan- based conditioning regimens are known to induce amenor- rhea and elevated gonadotropin levels in almost all post- menarcheal women and at least 50% of pre-pubertal
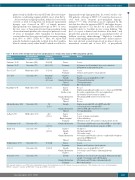
Table 4. Review of the literature on long-term complications in β-thalassemia major (β-TM) transplanted patients.
Study reference
Santarone39 2018 Santarone31 2017
Caocci38 2017 See25 2017
Chaudhury24 2017
Aldemir-Kocabas22 2014
La Nasa12 2013
Poomthavorn23 2013 Khalil21 2012
Di Bartolomeo11 2008 Li19 2004
De Sanctis18 2002
Uni/multicentric (number of patients)
Unicentric (122) Unicentric (75)
Multicentric (258) Unicentric (40)
Multicentric (176)
Unicentric (41)
Multicentric (109)
Unicentric (47) Unicentric (47)
Unicentric (90) Unicentric (32)
Unicentric (68)
Follow up, years [range]
24 [4-34] 24 [10-33]
11 [1-30]
Cumulative incidence at 10 years
7 [1-20]
5.4 [2-10]
22.8 [11-30]
6 [1-10.6]
7 [2-11.6]
15 [1-24] 5 [2-8.8]
3
End points
Cancer Pregnancy
Cancer Pregnancy
Diabetes Growth Gonadal dysfunction Thyroid Pregnancy
Cancer
Growth Cardiac, renal
Gonadal dysfunction Pregnancy Thyroid
Growth
Gonadal dysfunction Thyroid
Cancer
Kidney Organ transplant Pregnancy
Gonadal dysfunction
Diabetes Growth Heart Gonadal dysfunction
Thyroid
Cancer Pregnancy
Growth Gonadal dysfunction Diabetes
Growth
Gonadal dysfunction Pregnancy
Results
8 cases
40% women (n=15 including 2 after oocyte donation) 21% partners of male patients (n=8)
3 cases
6 women and 6 partners of male patients
2 cases
Mean decrease in height SDS of -0.84* ° 55% gonadal dysfunction°
7.5% hypothyroidism
One female patient
No case
Similar mean height and weight z-score > 4 years post HSCT/BL No cardiac complications, 20% renal complications (proteinuria/ elevated serum creatinine)
37% abnormal FSH or LH or testosterone level
No case
No case
Similar mean height SDS after HSCT and at BL° +0.6 mean increase in weight SDS *
14.6% low FSH, LH, testosterone or estradiol ° 10% hypothyroidism
4 cases
5 cases of chronic renal failure
2 (liver and kidney)
14% women (n=6), 17% partners of male patients (n=11)
77% females and 48% males: raised basal FSH (+/- raised LH) or low estradiol/ testosterone response to hCG
9% diabetes
52% final height SDS < -2
11% cardiac events
80% females and 36% males (absence of pubertal development and elevated FSH/LH level) °
11% hypothyroidism
2 cases
4 women and 2 partners of male patients
Mean decrease in height SDS of 0.59*
100% females and 50% males (abnormal puberty) 1 case
Growth rate deceleration after transplant. Median final height around -0.5 in females and -1 SDS in males
66% females and 37% males (abnormal puberty)
One female patient
SDS: standard deviation scores; FSH: follicle stimulating hormone; LH: luteinizing hormone; hCG: human chorionic gonadotropin. *After hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) compared to baseline at HSCT (BL). °Young age at HSCT is protective.
haematologica | 2018; 103(7)
1147