Page 118 - Haematologica June
P. 118
K. Kawamoto et al.
Epstein-Barr virus-DNA viral load in peripheral blood
A peripheral blood sample was obtained from each patient at diagnosis, in order to investigate the viral load by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction. A positive result was defined as an EBV-DNA viral load of ≥200 copies/mL, as previ- ously reported.18
Comparison of clinical features with pediatric-onset chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection and extra- nodal NK/T-cell lymphoma
To compare the clinical symptoms and prognosis of adult-, and pediatric-onset CAEBV, data from 75 patients younger than 15 years who developed CAEBV were extracted from the previously
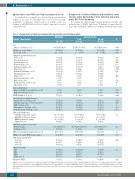
Table 1. Characteristics of adult-onset chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection patients.
All patients Infected-cell type Patients’ characteristics T-cell
P§
0.784
0.672
0.585
0.775 0.783 0.418 0.101 0.0202* 0.0119* 0.743
1 0.449 1 0.508 0.407 1
0.638
0.508 0.0814
0.758 0.268 1 0.101 0.407
na
na
na 0.180
0.127
na
0.723
NK-cell (n=54) (n=22) (n=32)
Sex
Male, n (%)/female, n (%)
31 (57.4)/23 (42.6)
39 (16-86)
22 (40.7)
35 (64.8) 31 (57.4) 28 (51.9) 22 (40.7) 21 (38.9) 21 (38.9) 11 (20.4) 11 (20.4) 8 (14.8) 5 (9.3)
2 (3.7) 1 (1.9) 1 (1.9)
4 (7.4)
2 (3.7) 17 (31.5)
15 (27.8) 26 (48.1) 40 (74.1) 22 (40.7) 25 (46.3)
320 (10-5120) <10 (<10-60) 40 (<10-320) 13 (24.1)
1×104(nd-1×106)
17 (31.5) 25/30 (81.3) 58 (2-487)
16 (29.6) 20 (37.0) 18 (33.3)
19 (35.2) 20 (37.0) 34 (61.8) 7/7 (100)
9 (16.7)
12 (54.5)/10 (45.5)
37 (19-86)
10 (0.455)
15 (68.2) 13 (59.1) 13 (59.1) 12 (54.5) 13 (59.1) 4 (18.2) 5 (22.7) 4 (18.2) 2 (9.1)
2 (9.1) 0 (0) 1 (4.5) 0 (0)
1 (4.5)
0 (0) 10 (45.5)
7 (31.8) 13 (59.1) 16 (72.7) 12 (54.5) 12 (54.5)
160 (10-2560) <10 (<10-40) 10 (<10-80) 4 (18.2)
1×104(2×102-1.1×106)
8 (36.4) 16/17 (94.1) 32 (2-435)
10 (45.5) 6 (27.2) 6 (27.2)
12 (63.2) 11 (55.0) 8 (23.5) 7/7 (100)
3 (13.6)
19 (59.4)/13 (40.6)
41 (16-78)
12 (0.545)
20 (62.5) 18 (56.3) 15 (46.9) 10 (31.3) 8 (25.0) 17 (53.1) 6 (18.8) 7 (21.9) 6 (18.8) 3 (9.4)
2 (6.3) 0 (0) 1 (3.1)
3 (9.4)
2 (6.3) 7 (21.9)
8 (25.0) 13 (40.6) 24 (75.0) 10 (31.3) 13 (40.6)
160 (40-5120) <10 (<10-60) 20 (<10-320) 9 (28.1)
1×104(nd-3.7×105)
9 (28.1) 9/13 (69.2) 61(3-487)
6 (18.7) 14 (43.8) 12 (37.5)
7 (36.8) 9 (45.0) 26 (76.5) na
6 (18.8)
Median age, years (range)
≥ 50 years, n (%)
Symptoms and involvement sites Fever, n (%)
Bone marrow, n (%) Splenomegaly, n (%) Hepatomegaly, n (%) Lymphadenopathy, n (%)
Skin rash, n (%)
Abdominal disturbance, n (%) Laryngopharynx, n (%)
Lung, n (%)
Gastrointestinal tract, n (%) Oral lesion, n (%)
Central nervous system, n (%) Myocarditis, n (%)
Past medical history
Hypersensitivity to mosquito bites, n (%) Hydroa vacciniforme, n (%)
ECOG PS high (2-4), n (%)
Laboratory test at initial diagnosis Anemia (Hb <10.5 g/dL), n (%) Thrombocytopenia (< 100×109/L), n (%) LDH elevation, n (%)
Transaminase, elevation, n (%)
Hemophagocytic syndrome, n (%)
EBV-related antibody to VCA-IgG, median titer (range) VCA-IgM, median titer (range) EBNA, median titer (range) Unknown, n (%)
EBV-DNA, in plasma (copies/mL) Median (range)
Unknown, n (%)
EBV monoclonality by Southern blot, n (%)
EBER+cell counts /HPF, median (range)
Histological classification9 A1, n (%)
A2, n (%) A3, n (%)
Immunophenotype CD4
CD8
CD56
TCRab (n = 7)
Allogeneic HSCT
1020
CAEBV: chronic active EBV infection; EBV: Eptein-Barr virus; EBNA: Epstein–Barr virus nuclear antigen 1; EBV-DNA: EBV-deoxyribonucleic acid; ECOG PS: Eastern Cooperative OncologyGroupPerformanceStatus;EBER:Epstein-Barrvirus-encodedRNA;nd:notdetected(EBV-DNA<2×102 copies/mL);HPF:highpowerfield;HSCT:hematopoieticstem cell transplantation; Hb: hemoglobin; LDH: lactate dehydrogenase; TCR: T-cell receptor; VCA: viral capsid antigen.*Statistically significant; na: not avalilable; P§: T-cell type versus NK-cell type.
haematologica | 2018; 103(6)